Rewritable material could help reduce paper waste
Advertisement
Even in today's digital age, the world still relies on paper and ink, most of which ends up in landfills or recycling centers. To reduce this waste, scientists have now developed a low-cost, environmentally friendly way to create printed materials with rewritable paper. Their report on the material, which is made out of tungsten oxide and a common polymer used in medicines and food.
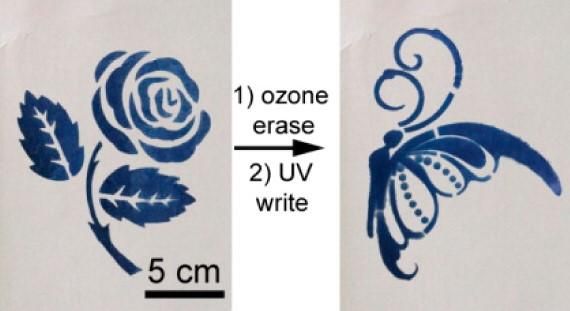
This rewritable paper can be 'printed' on with a stencil and UV light; it erases when exposed to oxygen in air or ozone.
American Chemical Society
The U.S. has been working to reduce paper waste by increasing recycling efforts for years. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, more paper is now recovered for recycling than almost all other materials combined. This saves energy, water, landfill space and greenhouse gas emissions. But even more waste could be avoided if consumers could reuse paper many times before recycling or trashing it. So far, however, such products under development often are made with toxic, expensive organic dyes. Ting Wang, Dairong Chen and colleagues wanted to come up with a better solution.
The researchers created a film by mixing low-toxicity tungsten oxide with polyvinyl pyrrolidone. To "print" on it, they exposed the material to ultraviolet light for 30 seconds or more, and it changed from white to a deep blue. To make pictures or words, a stencil can be used so that only the exposed parts turn blue. To erase them, the material can simply sit in ambient conditions for a day or two. To speed up the erasing, the researchers added heat to make the color disappear in 30 minutes. Alternatively, adding a small amount of polyacrylonitrile to the material can make designs last for up to 10 days. Testing showed the material could be printed on and erased 40 times before the quality started to decline.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Jing Wei, Xiuling Jiao, Ting Wang, and Dairong Chen; "Electrospun Photochromic Hybrid Membranes for Flexible Rewritable Media"; ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces; 2016
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.