Great strides for carbon capture using earth-abundant elements as photocatalytic system
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology have designed a CO2 reduction method based only on commonly occurring elements. Achieving a 57% overall quantum yield of CO2 reduction products, it is the highest performing system of its kind reported to date, raising prospects for cost-effective carbon capture solutions.
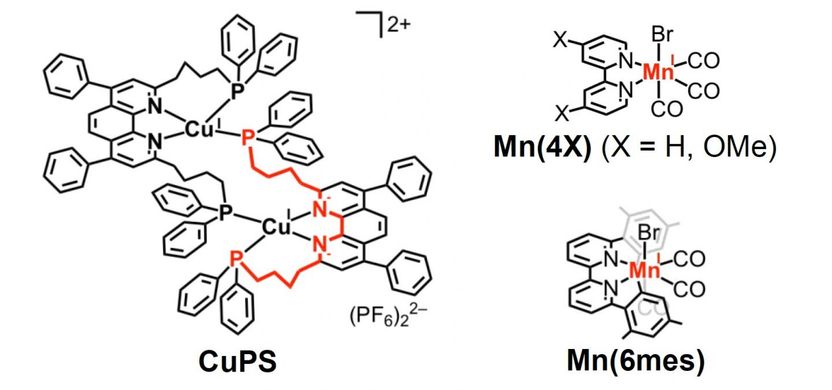
This is the structure of CuPS, the copper complex that behaves as a redox photosensitizer, and the manganese-based catalyst developed in the study.
Journal of the American Chemical Society
As global warming presents one of the biggest challenges to humanity in the 21st century, the quest to curb mounting CO2 emissions is more pressing than ever.
In a study Osamu Ishitani and colleagues at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology report a photocatalytic system that brings scientists closer to achieving artificial photosynthesis -- the goal of creating a sustainable system similar to the way that plants convert CO2 to useful energy by using earth abundant metals.
Although metal-complex photocatalytic systems have been reported for CO2 reduction, many of them used noble- and/or rare-metal complexes. Compared to these approaches that utilize rare metals (such as ruthenium and rhenium), the use of earth abundant metals is "greener" and inexpensive, and has thus attracted much interest.
A copper complex (CuPS) proved to be a stable and efficient redox photosensitizer, as decomposition was only 2% after 12 hours of irradiation. In addition, CuPS exhibited a much stronger reduction capability compared to other photosensitizers investigated to date.
The team reported that the total quantum yield of CO2 reduction products was 57%, the turnover number based on the manganese catalyst was over 1300 and the selectivity of CO2 reduction was 95%.
In particular, the figure of 57% is remarkable, as the researchers comment: "To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest quantum yield for CO2 reduction using abundant elements and the yield would be comparable to that obtained with rare metals."
The study highlights the way that incremental advances in chemistry may have a large impact on the wider goal of working towards a fossil-fuel-free future.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.




























































