Hydraulic fracturing chemical spills on agricultural land need scrutiny
hydraulic fracturing, a widely used method for extracting oil and gas from otherwise impenetrable shale and rock formations, involves not only underground injections composed mostly of water, but also a mixture of chemical additives. These chemicals range from toxic biocides and surfactants, to corrosion inhibitors and slicking agents, and many are also used by other industries.
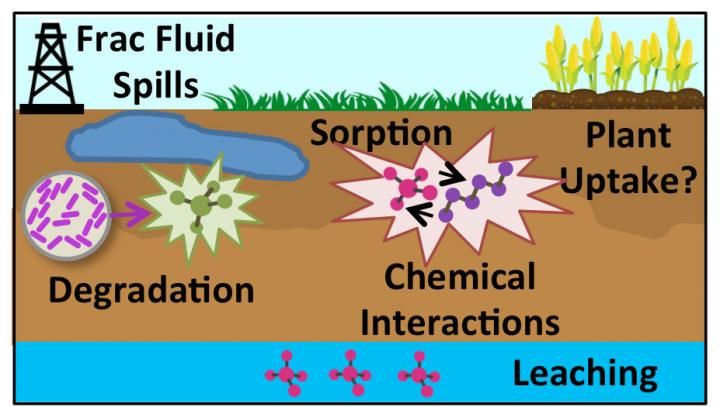
Colorado State University researchers set out to discover whether degradation of hydraulic fracturing chemicals in agricultural soil are affected by co-contamination.
Borch Lab/Colorado State University
A Colorado State University research team desired a deeper understanding of the fate of these chemicals when they are spilled accidentally during either transportation or production in oil and gas operations. These spills, especially in Colorado, often take place on or near agricultural lands.
The researchers set out to discover whether the degradation of these chemicals in agricultural soil are affected by co-contamination. The team consisted of Thomas Borch, a professor in the Department of Soil and Crop Sciences in the College of Agricultural Sciences, with joint appointments in civil and environmental engineering and chemistry; Jens Blotevogel, a research assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering; and their graduate student Molly McLaughlin.
In the paper, Borch, Blotevogel and McLaughlin cite 838 total hydraulic fracturing fluid spills in Colorado, reported to the Colorado Oil and Gas Conservation Commission in 2014. These spills only include those larger than five barrels of fluid when they happen within a well pad, and larger than one barrel when outside a well pad.
For their proof-of-concept experiments, the researchers used reactors to simulate chemical reactions and biodegradation of hydraulic fracturing additives spilled on agricultural soil. Later, they plan to test their conclusions at actual spill sites.
They tested three well-known organic chemicals: polyethylene glycol (PEG), a commonly used surfactant; glutaraldehyde, a biocide that prevents pipe corrosion from microbial activity; and polyacrylamide, a slicking agent that allows hydraulic fracturing fluid to better penetrate shale. They looked at how these chemicals interact both with each other, and with naturally occurring salts underground.
They found that the PEG (surfactant) by itself completely biodegrades within about 70 days, but that in combination with glutaraldehyde (biocide), the PEG stayed in the soil much longer. That biodegradation was fully inhibited by salt concentrations typical for oil and gas extraction activities.
"Our motivation for doing this is because the chemicals often come up as mixtures," Borch said. "While you may see biodegradation of a surfactant under normal circumstances, if you spill that together with a biocide that kills bacteria, maybe you don't break that surfactant down as quickly. And that's exactly what we see. If chemicals don't degrade as quickly, it gives them more time to be transported to groundwater or sensitive surface water."
They also looked at the degradation cycle of glutaraldehyde (biocide), which occurred within about two months. While polyacrylamide stuck around in the soil for six months, it covalently bonded with the glutaraldehyde, effectively lowering the toxicity of the biocide.
The bottom line is that more science is needed around how spilled chemicals interact with each other and the underground chemical environment - and this applies not just to oil and gas extraction, but to many industrial processes, the researchers say. Such follow-up studies could lead to better understanding of the potential uptake of pollutants in crops, or contamination of groundwater and surface water, with the ultimate goal of helping improve human health risk assessment of spills.
"We cannot say our findings are valid for all the different chemicals used worldwide in hydraulic fracturing," Blotevogel said. "There are probably 1,000 different chemicals used globally, and they all behave very differently with respect to how they are broken down."
Borch and Blotevogel previously published a comprehensive review of the biocide toxicity in hydraulic fracturing fluids and have worked together for almost nine years. The ES&T study was supported primarily by CSU's School of Global and Environmental Sustainability (SoGES), a grant from the CSU Water Center, and by the Borch-Hoppess Fund for Environmental Contaminant Research.
Original publication
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

FASTEC GmbH - Paderborn, Germany

Biofuel for ships - Diesel and gasoline sourced from renewables produces a lot less greenhouse gas

Zhejiang Cathaya Light Products and Textiles Imp. & Exp. Co., Ltd. - Hangzhou, Zehjiang, China

Ecolab GmbH - Wien, Austria
Solvay has successfully commisioned the largest PEM fuel cell at Solvin's Antwerp plant - H2 powered industrial demonstration 1 MW Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
LANXESS opens butyl rubber plant in Singapore
Caliper Life Sciences Awarded EPA Contract for Multi-Year, Multi-Million Dollar Tox Program - Caliper Discovery Alliances & Services Unit to Test Environmental Chemicals
New company brings together microbes & genomics to improve health, agriculture & industry - The biotechnology company Microomics is a spin-off from the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) and the Catalan Institute for Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA) specialized in microbiome analysis

gowitec - Wiehl, Germany