Combining nanotextured surfaces with the Leidenfrost effect for extreme water repellency
Advertisement
Combining superhydrophobic surfaces with Leidenfrost levitation--picture a water droplet hovering over a hot surface rather than making physical contact with it--has been explored extensively for the past decade by researchers hoping to uncover the holy grail of water-repellent surfaces.

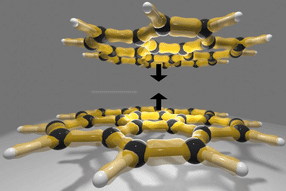
A liquid droplet bouncing on a nanotextured surface powered by the Leidenfrost levitation and the Cassie state: The kinetic energy is transferred into the surface energy with small energy dissipation by the Cassie surface, which facilitates the droplet's rebound repeatedly until the capillary pressure outweighs the vapor pressure.
Lee and Song
In a new twist, a group of South Korean researchers from Seoul National University and Dankook University report an anomalous water droplet-bouncing phenomenon generated by Leidenfrost levitation on nanotextured surfaces.
"Wettability plays a key role in determining the equilibrium contact angles, contact angle hysteresis, and adhesion between a solid surface and liquid, as well as the retraction process of a liquid droplet impinged on the surface," explained Doo Jin Lee, lead author, and a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Materials and Engineering at Seoul National University.
Nonwetting surfaces tend to be created by one of two methods. "First, textured surfaces enable nonwettability because a liquid can't penetrate into the micro- or nano-features, thanks to air entrapment between asperities on the textured materials," Lee said.
Or, second, the Leidenfrost effect "can help produce a liquid droplet dancing on a hot surface by floating it on a cushion of its own vapor," he added. "The vapor film between the droplet and heated surface allows the droplet to bounce off the surface--also known as the 'dynamic Leidenfrost phenomenon.'"
Lee and colleagues developed a special "nonwetting, nanotextured surface" so they could delve into the dynamic Leidenfrost effect's impact on the material.
"Our nanotextured surface was verified to be 'nonwetting' via thermodynamic analysis," Lee elaborated. "This analytical approach shows that the water droplet isn't likely to penetrate into the surface's nanoholes, which is advantageous for designing nonwetting, water-repellant systems. And the water droplet bouncing was powered by the synergetic combination of the nonwetting surface--often called a 'Cassie surface'--and the Leidenfrost effect."
By comparing the hydrophobic surface and nanotextured surface, the group discovered that enhanced water droplet bouncing was created by the combined impact of the Leidenfrost levitation and the nonwetting Cassie state.
"A thermodynamic approach predicts the nonwettability on the nanotextured surface, and a scaling law between the capillary and vapor pressure of the droplet explains the mechanism of the dynamic Leidenfrost phenomenon," said Lee.
These findings should "be of value for a wide range of research areas, such as the study of nonwetting surfaces by the Leidenfrost effect and nanotextured features, enhanced liquid droplet bouncing, and film boiling of liquid droplets on heated Cassie surfaces," he added.
Significantly, the group's work furthers the fundamental understanding of the dynamic Leidenfrost droplet levitation and droplet-bouncing phenomena on hydrophobic and nanoengineered surfaces. This means that it will be useful for developing highly water-repellant surfaces for industrial applications such as self-cleaning windows, windshields, exterior paints, anti-fouling coatings, roof tiles, and textiles in the future.
"Our future work will focus on developing multiscale structures with microscale and nanoscale regularities, and explore the nonwetting characteristics of their surfaces with the dynamic Leidenfrost effect," Lee noted.