From the scent of roses to nylon and plastics
Enzyme for plastics production from renewable raw materials
Beguiling scents, sober facts: scents emanating from plants are almost always monoterpenes and monoterpene alcohols, the essential oils of plants are natural hydrocarbon compounds. For instant, geraniol is the tempting fragrant alcohol of roses. Researchers of the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen have published in 2010 the discovery of an enzyme, which converts the rose-scented geraniol in the coriander-scented coriandrol ((S) -linalool) and further in the hop-scented myrcene.
Sina Weidenweber und Ulrich Ermler, Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysik, Frankfurt

Sina Weidenweber, Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysik, Frankfurt

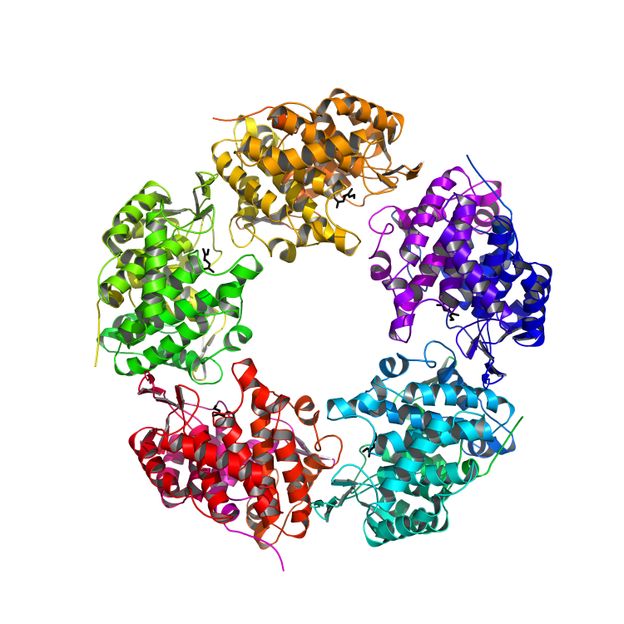
However, this enzyme, the linalool dehydratase/isomerase is also capable of forning butadiene from natural raw materials, such as fermentation products. Butadiene is a key compound in the manufacturing process of plastics. Now, the researchers were able to elucidate the exact three-dimensional structure of the enzyme and the binding sites of geraniol and myrcene on the enzyme, an important milestone on the way from the petrochemical industry towards the energy-economic use of natural resources.
Butadiene and isoprene: important intermediates in plastics production
Butadiene and isoprene are intermediates for nylon production, high-melting plastics (ABS polymers) and rubber products. So far butadiene is produced elaborately by cracking of petroleum. Therefore, the chemical industry has a great interest in energy-economic alternatives to butadiene synthesis.
Over 10 million tons of butadiene and isoprene are annually produced under considerable energy consumption from fossil fuels, a market of over 15 billion euros. A few years ago, high oil prices and increasing demand triggered an intensive search for alternative production methods. The switch to renewable raw materials and an energy-poor production method requires biocatalysts, and the catalytic properties of linalool dehydratase/isomerase are ideal for this task. Based on the discovery of the enzyme by Bremer researchers in 2010, a considerable number of patent applications and patents have been published that describe the use of this enzyme in the production of butadiene and isoprene.
Discovery of the substrate binding on the enzyme
To make effective use of the enzyme in the industry, you have to know the internal architecture and how and where the actual reaction takes place. Now Sina Weiden Weber and Ulrich Ermler from the Max Planck-Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt and Robert Marmulla and Jens Harder from the Max Planck-Institute for Marine Microbiology in Bremen succeeded in the elucidation of the molecular structure of the enzyme. The enzyme is composed of five identical subunits and has a unique binding site for monoterpene alcohols. "In recent years it was very gratifying to see the rapid use of our results from basic research in applied industrial research. The linalool dehydratase/isomerase structure, the precise knowledge of geraniol and myrcene-binding sites and the insight into the catalytic mechanisms will now enable industrial companies to optimize this actually monoterpenes degrading enzyme for the biotechnological production of butadiene and isoprene. "says Jens Harder.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




























































