Argonne and Los Alamos National Laboratories develop more affordable fuel cell components
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne and Los Alamos national laboratories have teamed up to support a DOE initiative through the creation of the Electrocatalysis Consortium (ElectroCat), a collaboration devoted to finding an effective but cheaper alternative to platinum in hydrogen fuel cells.
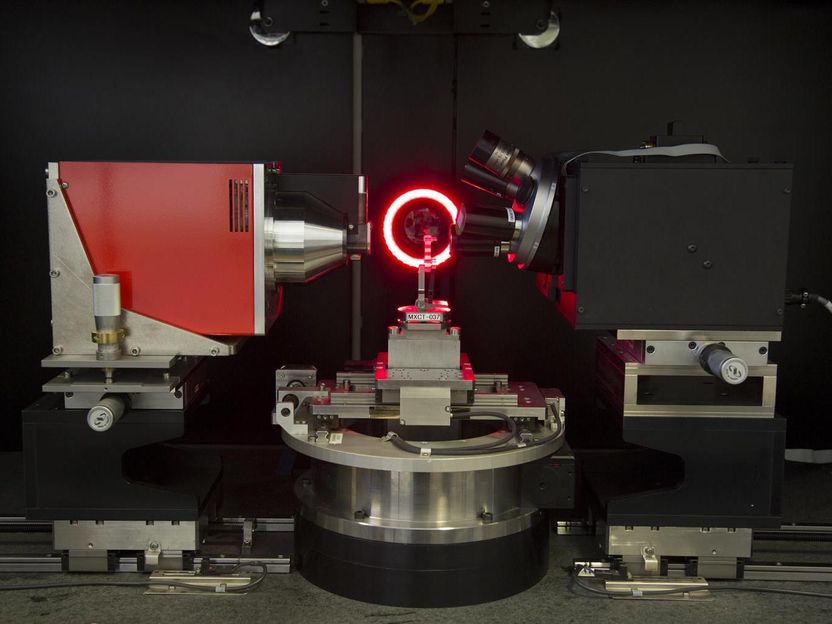
An X-ray computed microtomograph for non-destructive 3-D-imaging of fuel cell components is among the tools that will be of use in the ElectroCat fuel cell project.
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Announced last week, ElectroCat is dedicated to finding new ways to replace rare and costly platinum group metals in fuel cell cathodes with more accessible and inexpensive substitutes - such as materials based on the earth-abundant metals iron and cobalt.
The heart of the automotive fuel-cell power system is the fuel cell stack, which is where the platinum is used. "Platinum is a precious metal, which means that it is both expensive and difficult to get," said Piotr Zelenay, a Los Alamos National Laboratory fellow and lead scientist on the Los Alamos component of the consortium.
About half of the total cost of a typical automotive fuel cell stack comes directly from the cost of the platinum metal in the electrode catalysts. "In order to make hydrogen fuel cell cars an affordable reality, we need to find a way to either significantly reduce the amount of platinum needed or completely replace platinum with less expensive materials," said Debbie Myers, an Argonne senior chemist who will serve as the Argonne lead in the consortium.
"The challenge for us and for industry is to develop new catalysts that meet targets for activity, durability, cost and ease of integration into membrane electrode assemblies," Zelenay added. "Thankfully, the national laboratory system includes the people who have the skills to address these issues."
ElectroCat is one of four consortia that make up DOE's Energy Materials Network (EMN). The EMN will facilitate industry access to the unique scientific and technical resources available at the national laboratories, enabling manufacturers to bring advanced materials to market more quickly.
"At the core of virtually every problem we tackle at the Energy Department, there is a materials challenge," said Deputy Assistant Secretary for Transportation Reuben Sarkar. "Whether it's a better battery, a lighter material or a new fuel cell technology - materials underlie almost everything that we do, so shifting the paradigm from traditional materials research to an acceleration-focused strategy is crucial."
The partnership between Argonne and Los Alamos that forms the core of ElectroCat involves the study, creation and implementation of possible alternatives to platinum-based electrodes through material- development efforts headed by Los Alamos and accelerated by the high-throughput, combinatorial, characterization and electrode performance modeling capabilities at Argonne, as well as by applying a high-performance supercomputer to model new catalyst structures at Los Alamos.
In developing new materials to be explored, researchers at Los Alamos will bring to bear 15 years of experience in platinum-free catalyst design, synthesis, characterization and testing. In addition, Los Alamos can apply multi-scale modeling techniques that leverage world-class computing facilities to design catalysts with optimal activity, selectivity and durability.
Once the potential replacement candidate materials are identified, scientists in the consortium can examine materials using a number of different methods, including X-ray imaging and spectroscopy techniques at Argonne. Argonne researchers can also investigate samples in a number of different environments that replicate how they would function in real-world scenarios.
By combining the expertise and capabilities at Argonne and Los Alamos, in partnership with the private sector and universities, researchers expect to accelerate the development and implementation of platinum-free catalysts in fuel cells.
"The acceleration of progress in electrocatalysis without platinum will depend on focused catalyst design, guided by multi-scale modeling methods and facilitated by high-throughput methods for synthesis and screening," said Zelenay. "This partnership will integrate the strengths of both laboratories for this purpose."
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

Gilson MyPIPETMAN Select and MyPIPETMAN Enterprise Pipettes by Gilson
Grab the Gilson pipettes with your name and favorite colors!
Customise Your Pipettes to Fit Your Research

Systec H-Series by Systec
Safe, reproducible and validatable sterilization of liquids, solids and waste
Autoclaves with 65-1580 liters usable space, flexibly expandable for various applications

Whatman™ folded filter papers by Cytiva
Whatman folded filter papers
Convenient folded formats speed up your sample preparation

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

ARGUS - Additive Plastics GmbH - Büren, Germany

E+E Elektronik Ges.m.b.H. - Engerwitzdorf, Austria

BASF Argentina S.A. - Buenos Aires, Argentina
Lehigh University professor receives Astellas Award for arsenic groundwater remediation efforts

L&R Kältetechnik GmbH & Co.KG - Sundern, Germany
Deep Earth heat surprise

Bohncke GmbH - Hünstetten-Wallbach, Germany

TRM Systec - Ettringen, Germany