Physicists offer theories to explain mysterious collision at Large Hadron Collider
Advertisement
Physicists around the world were puzzled recently when an unusual bump appeared in the signal of the Large Hadron Collider, the world's largest and most powerful particle accelerator, causing them to wonder if it was a new particle previously unknown, or perhaps even two new particles. The collision cannot be explained by the Standard Model, the theoretical foundation of particle physics.
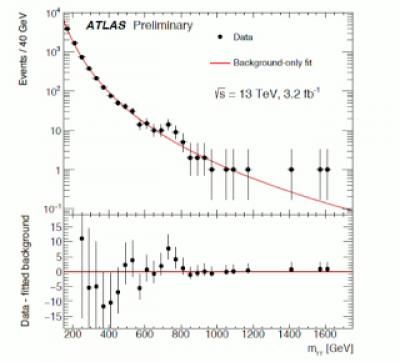
This graph illustrates black dots that show events in experiment records compared along a red line that depicts the number expected through Standard Model processes. Two black dots don't fall in with the red line. Adam Martin says the bump at 750 is "the most exciting."
Adam Martin
Adam Martin, assistant professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame, said he and other theoretical physicists had heard about the results before they were released on Dec. 15, and groups began brainstorming, via Skype and other ways, about what the bump could mean if confirmed -- a long shot, but an intriguing one.
This graph illustrates black dots that show events in experiment records compared along a red line that depicts the number expected through Standard Model processes. Two black dots don't fall in with the red line. Adam Martin says the bump at 750 is "the most exciting."
"It was so weird that people were forced to chuck their favorite theories and start from scratch," Martin says. "That's a fun area of particle physics. We're looking into the unknown. Is it one new particle? Is it two new particles?"
The paper considers four possible explanations for the data, including the possibility that it could indicate a heavier version of the Higgs boson, also commonly known as "the God particle." Further research could yield mundane explanations, Martin says, and the excitement could fade as it has many times in his career. Or it could open up new insights and call for new models.
"People are still cautiously optimistic," he says. "Everybody knows that with more data, it could just go away. If it stays, it's potentially really, really, really exciting."























































