Researchers take first steps to create biodegradable displays for electronics
Advertisement
University of Missouri researchers are on the path to creating biodegradable electronics by using organic components in screen displays. The researchers' advancements could one day help reduce electronic waste in the world's landfills.
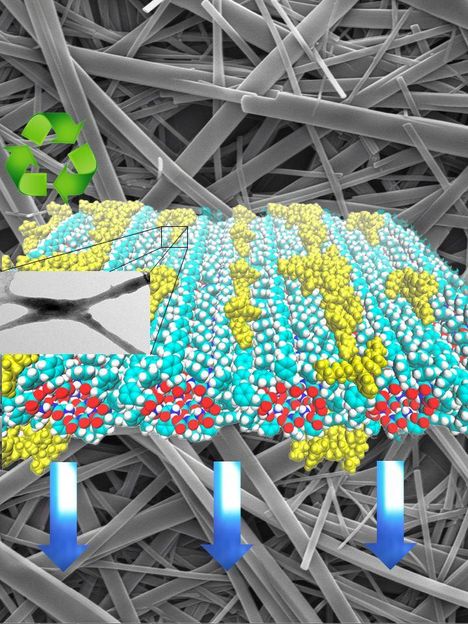
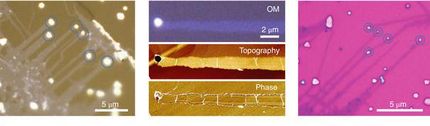
The illustration shows a theoretical simulation of the distribution of the polymer on peptide nanotubes and an electron microscopy image of the nanocomposite.
Suchi Guha, University of Missouri
"Current mobile phones and electronics are not biodegradable and create significant waste when they're disposed," said Suchismita Guha, professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the MU College of Arts and Science. "This discovery creates the first biodegradable active layer in organic electronics, meaning--in principle--we can eventually achieve full biodegradability."
Guha, along with graduate student Soma Khanra, collaborated with a team from the Federal University of ABC (UFABC) in Brazil to develop organic structures that could be used to light handheld device screens. Using peptides, or proteins, researchers were able to demonstrate that these tiny structures, when combined with a blue light-emitting polymer, could successfully be used in displays.
"These peptides can self-assemble into beautiful nanostructures or nanotubes, and, for us, the main goal has been to use these nanotubes as templates for other materials," Guha said. "By combining organic semiconductors with nanomaterials, we were able to create the blue light needed for a display. However, in order to make a workable screen for your mobile phone or other displays, we'll need to show similar success with red and green light-emitting polymers."
The scientists also discovered that by using peptide nanostructures they were able to use less of the polymer. Using less to create the same blue light means that the nanocomposites achieve almost 85 percent biodegradability.
"By using peptide nanostructures, which are 100 percent biodegradable, to create the template for the active layer for the polymers, we are able to understand how electronics themselves can be more biodegradable," Guha said. "This research is the first step and the first demonstration of using such biology to improve electronics."