Half diamond, half cubic boron, all cutting business
diamonds are forever, except when they oxidize while cutting through iron, cobalt, nickel, chromium, or vanadium at high temperatures. Conversely, cubic boron nitride possesses superior chemical inertness but only about half of the hardness of diamonds. In an attempt to create a superhard material better suited for a wide variety of materials on an industrial scale, researchers at Sichuan University in Chengdu, China, have created an alloy composed of diamonds and cubic boron nitride (cBN) that boasts the benefits of both.
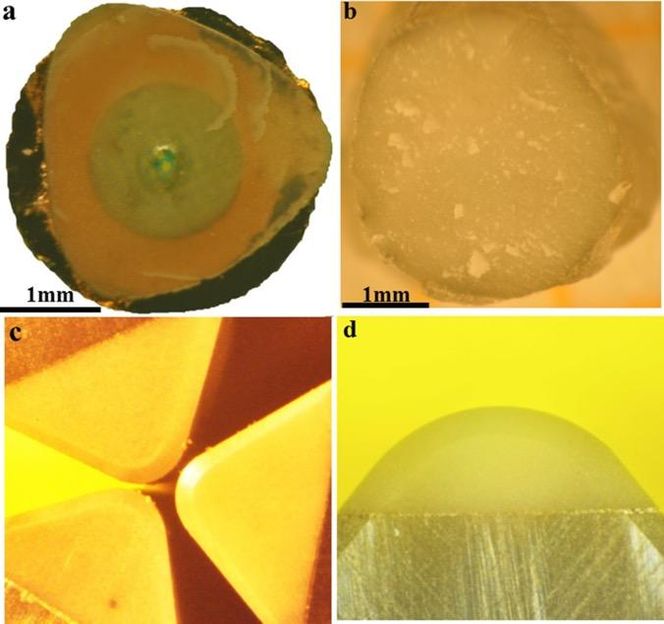
A and B show a bulk diamond-cBN alloy samples synthesized at 20 GPa/2200 °C with a diameter of
D. W. He/SCU
"Diamond and cubic boron nitride could readily form alloys that can potentially fill the performance gap because of their affinity in structure lattices and covalent bonding character," said Duanwei He, a professor at Sichauan University's Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics. "However, the idea has never been demonstrated because samples obtained in previous studies are too small to test their practical performance."
To synthesize diamond-cBN alloys, the researchers subjected a homogenous mixture of diamond and cubic boron nitride powder to a vacuum furnace at 1300 K for two hours, then pressed the material into 3.5 millimeter pellets under pressure greater than 15 gigapascals and temperatures above 2000 K. The pellets were then polished and sharpened into cutting implements.
The researchers tested the cutting performances of their alloy on hardened steel and granite bars on a computer numerical controlled lathe. They found that the diamond-cBN alloy rivaled polycrystalline cubic boron nitride's wear and tool life on the steel samples, and exhibited significantly less wear when cutting through granite. The alloy also demonstrated a more preferable high-speed cutting performance than either polycrystalline CBN or commercial polycrystalline diamonds.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.