Sol-gel capacitor dielectric offers record-high energy storage
Using a hybrid silica sol-gel material and self-assembled monolayers of a common fatty acid, researchers have developed a new capacitor dielectric material that provides an electrical energy storage capacity rivaling certain batteries, with both a high energy density and high power density.
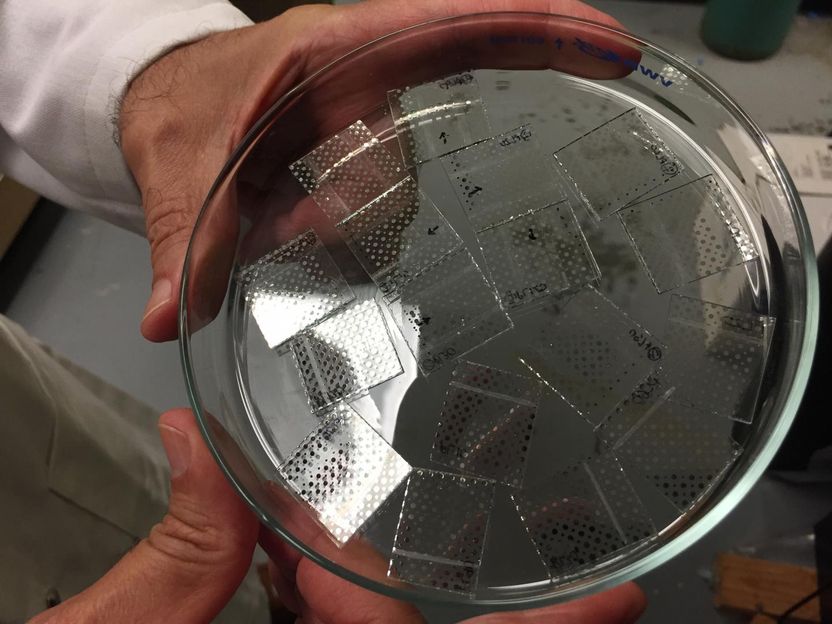
These are samples of the new hybrid sol-gel material are shown placed on a clear plastic substrate for testing.
John Toon, Georgia Tech
If the material can be scaled up from laboratory samples, devices made from it could surpass traditional electrolytic capacitors for applications in electromagnetic propulsion, electric vehicles and defibrillators. Capacitors often complement batteries in these applications because they can provide large amounts of current quickly.
The new material is composed of a silica sol-gel thin film containing polar groups linked to the silicon atoms and a nanoscale self-assembled monolayer of an octylphosphonic acid, which provides insulating properties. The bilayer structure blocks the injection of electrons into the sol-gel material, providing low leakage current, high breakdown strength and high energy extraction efficiency.
"Sol-gels with organic groups are well known and fatty acids such as phosphonic acids are well known," noted Joseph Perry, a professor in the School of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the Georgia Institute of Technology. "But to the best of our knowledge, this is the first time these two types of materials have been combined into high-density energy storage devices."
It has been challenging to find a single dielectric material able to maximize permittivity, breakdown strength, energy density and energy extraction efficiency.
Perry and colleagues in Georgia Tech's Center for Organic Photonics and Electronics (COPE) had been working on other capacitor materials to meet these demands, but were not satisfied with the progress. The hybrid sol-gel materials had shown potential for efficient dielectric energy storage because of their high orientational polarization under an electric field, so the group decided to pursue these materials for the new capacitor applications.
Using an aluminized mylar film coated with the hybrid sol-gel capacitor material, they showed that the capacitor could be rolled and re-rolled several times while maintaining high energy density, demonstrating its flexibility. But they were still seeing high current leakage. To address that, they deposited a nanoscale self-assembled monolayer of n-octylphosphonic acid on top of the hybrid sol-gel. Less than a nanometer thick, the monolayer serves as an insulating layer.
In their structures, the researchers demonstrated maximum extractable energy densities up to 40 joules per cubic centimeter, an energy extraction efficiency of 72 percent at a field strength of 830 volts per micron, and a power density of 520 watts per cubic centimeter. The performance exceeds that of conventional electrolytic capacitors and thin-film lithium ion batteries, though it doesn't match the lithium ion battery formats commonly used in electronic devices and vehicles.
"This is the first time I've seen a capacitor beat a battery on energy density," said Perry. "The combination of high energy density and high power density is uncommon in the capacitor world."
"What we see when we apply an electric field is that the polarization response - which measures how much the polar groups line up in a stable way with the field - behaves in a linear way," said Perry. "This is what you want to see in a capacitor dielectric material."
The next step will be to scale up the materials to see if the attractive properties transfer to larger devices. If that is successful, Perry expects to commercialize the material through a startup company or SBIR project.
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.

Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.