Silica 'spiky screws' could enhance industrial coatings, additive manufacturing
It took marine sponges millions of years to perfect their spike-like structures, but research mimicking these formations may soon alter how industrial coatings and 3-D printed to additively manufactured objects are produced.
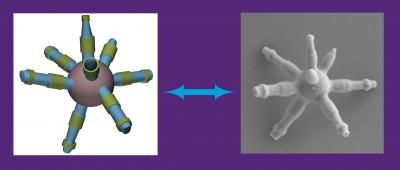
The screw-like spikes grown from a spherical silica particle depicted above may alter the internal strength of materials used in industrial coatings, 3-D printing and other additively manufactured objects.
ORNL
A molecular process developed by researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, paves the way for improved silica structure design by introducing microscopic, segmented screw-like spikes that can more effectively bond materials for commercial use.
The study, conducted by Jaswinder Sharma and his colleagues Panos Datskos and David Cullen, has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. Authors said other applications of the screw-like spikes could include coatings for eyeglasses, television screens, commercial transportation and even self-cleaning windows and roofs in rural and urban environments.
Created by emulsion droplets applied to a silica particle's surface, the new, segmented spikes offer an alternative tool for material scientists and engineers that can better maintain and fuse bonds within a variety of microstructures.
Combined with tetraethyl orthosilicate, an additive molecule, the emulsion droplets begin to produce rod-like spikes whose growth can be controlled for silica structures and configured into new materials.
The development of a segmented spike comes as an enhanced version of previous research conducted by the team. Sharma explained that the screw-like shape of these spikes was achieved when temperature control was incorporated with the spike growth on preformed particles
In previous experiments, the spikes appeared in a rod-like, linear shape, preventing the silica from bending into the diverse shapes Sharma's team sought to create from the particle seeds.
"If you try to use these linear ones, they will lie down like a pen does," Sharma said. "They won't stand. But if you have the segmented, spiky screws or smooth spiky screws, they will stand. They are the better shape."
According to the authors, the segmented spike's most direct application rests on interface engineering and the ongoing advancements in additive manufacturing, another significant ORNL research area.
With the spikes' new shape, materials for bonding layers can maintain a stronger internal structure, lasting longer than previously used approaches.
Authors also experimented with a hybrid structure made from silica and titania, confirming that the silica-based spike growth can work for other oxide materials as well.
While they noted the hybrid's use in future processes, the authors said the spectrum of possibilities remains wide open for future researchers to explore.
"We actually developed a process to create new structures, but we didn't focus on one application when we did that," Sharma said. "We looked at a range of applications where this could fit, and we are now trying to explore all those directions."
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
OCA 200 by DataPhysics
Using contact angle meter to comprehensively characterise wetting behaviour, solids, and liquids
With its intuitive software and as a modular system, the OCA 200 answers to all customers’ needs

Tailor-made products for specific applications by IPC Process Center
Granulates and pellets - we develop and manufacture the perfect solution for you
Agglomeration of powders, pelletising of powders and fluids, coating with melts and polymers
Dursan by SilcoTek
Innovative coating revolutionizes LC analysis
Stainless steel components with the performance of PEEK - inert, robust and cost-effective

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.



























































