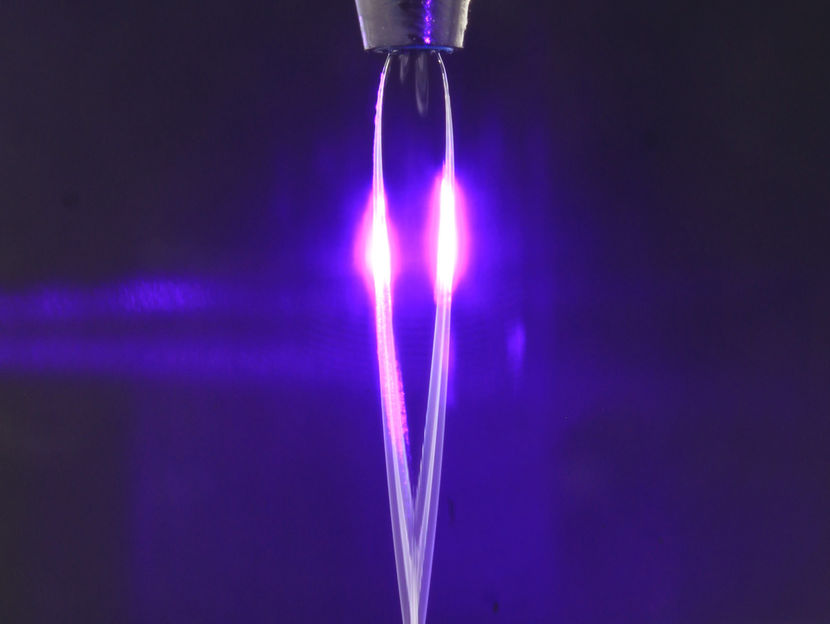
Speed at its limits
Physicists develop ultra-fast semiconductor nano-lasers
One thousand billion operations per second – this peak value is achieved by semiconductor nano-lasers developed by physicists at the University of Jena together with their colleagues from Imperial College London. As the researcher report in the current issue of the journal of „Nature Physics“, they are capable of producing the fastest lasers to date.
The fastest, in this case means the speed at which the laser can be turned on and off and not the length of laser pulse, as Prof. Dr. Carsten Ronning from the University of Jena clarifies. “While the fastest lasers typically need several nanoseconds for one cycle our semiconductor nano-laser only needs less than a picosecond and is therefore a thousand times faster,“ the solid state physicist continues.
For their nano lasers the researchers use tiny wires made of zinc oxide. These wires have diameters of a few hundreds of nanometres – around a thousandth of the diameter of human hair - and are about a few micro meters long. Their properties make these nanowires an active laser medium and a resonator at the same time. “Light is being reflected at the ends of the nanowire, similar to a mirror, and is then amplified while propagating through the nanowire,“ says Robert Röder. The PhD student in Prof. Ronning’s team is one of the authors on this current publication.
For the researchers the concept of using nanowires as a laser is not new. However, the new idea in this publication is the possibility to fundamentally modify the speed of these lasers. To this end the physicists combined the semiconductor with a metallic layer, leaving only a 10 nanometer thin gap layer between both in which the light field is constricted. “This is how light-matter interactions are accelerated,“ says Robert Röder. This is not only “world record“ regarding the switching speed. “Most likely we also achieved the maximum possible speed, at which such a semiconductor laser can be operated“. Applications for these ultrafast und nanometre small lasers are especially optical transistors and sensors. “Using such tiny sensors single molecules or microbes can be detected in medical diagnostics“, emphasizes Prof. Ronning.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

SprayMaster inspex by LaVision
Quality Control for Your Spraying Process Through Digital Spray and Particle Analysis
Reliable, Automated, Digital - The Geometry Measurement of Your Spraying Process in Real Time

FireSting-PRO by PyroScience
New fiber optic measuring device: Precise measurements even in the smallest volumes
Measure pH, oxygen and temperature even under sterile conditions

VEGAPULS | VEGABAR | VEGASWING by VEGA Grieshaber
Cyber-safe level measurement - here's how it works
Find out more about the unique sensor for liquid and solid media

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.

Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.
Last viewed contents
BASF to reorganize its paper, water, oilfield and mining businesses
Wacker Boosts Supply for Surface Coating Resins

Fueling the future - Scientists promote new method of algal hydrogen production
Ultraheavy precision polymers - Controlled photoenzymatic RAFT polymerization of nonconjugated polymers
New technique for detecting mold contamination in homes and other buildings
Gems_of_Sri_Lanka
Category:ADP_receptor_inhibitors

The dance of atoms
Clariant installs additional capacity at its emulsion plant in Argentina




























































