Terahertz dance of amino acids
RUB chemists explain the fingerprint of dissolved glycine in the Terahertz range
Chemists at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have, for the first time, completely analysed the fingerprint region of the Terahertz spectrum of a biologically relevant molecule in water, in this case, an amino acid. By combining spectroscopy and molecular-dynamics simulations, they rendered the motion of the most basic amino acid, glycine, visible in an aqueous solution. Their results have disproved the long-standing theory that frequencies in the Terahertz range provide no information regarding the amino acid’s motion.
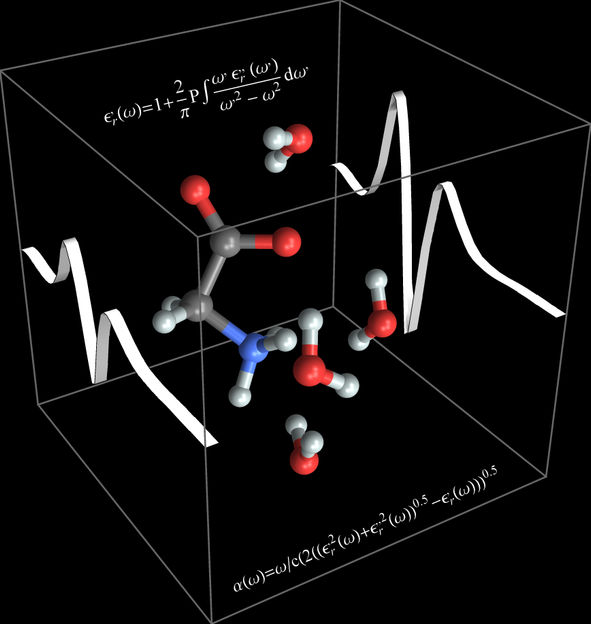
Terahertz dance of the molecules: The molecular motion of the amino acid glycine and its surrounding water molecules result in the formation of characteristic bands in the Terahertz spectrum.
© RUB, Illustration: Decka, Havenith
Representing molecular motion by means of Terahertz spectroscopy
Researchers use Terahertz (THz) spectroscopy to send short radiation pulses into a sample of interest. The Terahertz range covers wavelengths of one to ten THz (0.3 millimetres to 30 micrometres) and extends between the infrared and the microwave range. The sample, in this case a mixture of water and glycine, partially absorbs the radiation, forming an absorption pattern, which is represented by chemists in the form of a spectrum. Certain areas of the spectrum, so-called bands, describe the motions of molecular bonds. Individual atoms in a molecule are not bonded rigidly; rather, they are permanently in motion. Complex computer simulations contribute significantly to analysing the spectra, as it is not always easy to decipher which individual bands of a spectrum correlate with which molecular motions.
THz analysis renders glycine motion in water visible
The RUB team has proved that THz analysis may be used to represent both the motion inside the glycine molecule and the motion of the glycine molecule together with its bound water molecules. The bands in the Terahertz spectrum, moreover, reflected the glycine's opening and closing motion. The spectrum also incorporated the motion of hydrogen bridges between the glycine and its bound water molecules. "The interaction between ab initio molecular-dynamics simulations and Terahertz spectroscopy provides us with an excellent instrument for tracking and understanding solvation processes on the molecular level," says Martina Havenith-Newen, Head of the Department of Physical Chemistry II.
Original publication
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!