Tin for faster chips
To process and save data more and more quickly, to build even smaller and more powerful chips: these are the goals pursued by numerous research teams around the world. For some years now, one special material class has been at the heart of their efforts, so-called topological insulators. Within these, electrons automatically separate according to their respective spin orientation, entirely without the use of electric or magnetic fields.
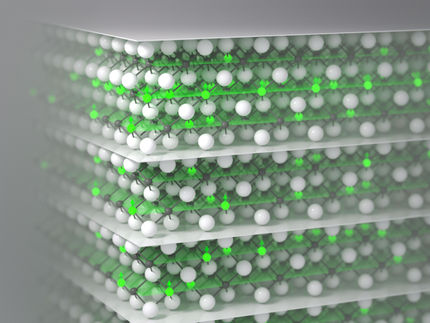
Topological insulator: in a layer of tin, electrons separate automatically according to the orientation of their spin, symbolized by arrows.
Markus R. Scholz/Arjun Kartha
“This property is of far-reaching significance,” explains Professor Ralph Claessen from the Institute of Physics at the University of Würzburg: “If you apply electrical contacts to topological insulators, you can build circuits that transmit information coded with the spin orientation.” This new data transmission method is no longer based on the transport of electrical charges. It is therefore much faster and more reliable.
Why tin represents progress
Würzburg physicists have now, for the first time, succeeded in creating topological insulators made from tin, a simple and readily available material. “This makes production much easier because insulators like these have only ever been made from complex chemical compounds or hazardous materials,” says Claessen’s colleague Jörg Schäfer.
The physicists are presenting their findings in the journal “Physical Review Letters”. They have achieved their success as part of an international collaboration with teams from Switzerland and the USA as well as from the Jülich Research Center. At Würzburg’s Institute of Physics, Professor Laurens Molenkamp also works with topological insulators, and successfully so: a few years ago, motivated by theoretical predictions, he became the first person to verify the unusual properties of this material class in a series of experiments.
How the topological insulator came about
In the new experiments under Ralph Claessen’s chairmanship and Jörg Schäfer’s leadership, thin layers of tin were vapor-deposited onto a semiconductor substrate extremely slowly. An orderly crystal lattice of tin atoms formed, identical to that of diamond.
“Experiments then revealed that this layer has the unusual properties we were looking for: the spins of the electrons are sorted into two directions with opposite magnetic needle orientation, and the two groups move in opposite directions,” says Schäfer. This was proven with spin-resolved photoemission.
“This has enabled us to show, for the very first time, that the phenomenon of automatic spin separation also exists in a simple, elementary crystal lattice,” enthuses Schäfer. As a result, he believes that the production of practical topological insulators is now tantalizingly close. The new experiments were underpinned by theoretical observations that Würzburg physics professor Werner Hanke made with colleagues in Jülich.
Next steps for the physicists
Since the spin separation in the tin lattice itself can now be reliably produced, the physicists next want to explore and optimize the conductive behavior of complete structures with electrical contacts.
Initial demonstrations of spin transport in layers with topological materials have already worked at temperatures well below freezing. So, for practical application, a number of technological issues still need to be clarified, including the realization of circuits that work without cooling. For this purpose, the Würzburg physicists are now working intensively together, pooling their expertise in material production and analysis.
Original publication
Original publication
A. Barfuss, L. Dudy, M. R. Scholz, et al., “Elemental Topological Insulator with Tunable Fermi Level: Strained alpha-Sn on InSb(001)”, Physical Review Letters 111, 157205 (October 2013)
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Microfluidic applications centre Dolomite exceeds expectations
Ultra-thin crystals as light sources in lasers - Laser emission demonstrated at room temperature: semiconductors consisting of three atomic layers could form the basis for innovative lasers

Universal solvent no match for new self-healing sticky gel
Blue phosphorus - mapped and measured for the first time
Vitamin_O