Newly discovered mechanism propels micromotors
Tiny clusters of particles zip forward, spin, or circle depending on their shape
Advertisement
Scientists studying the behavior of platinum particles immersed in hydrogen peroxide may have discovered a new way to propel microscopic machines.
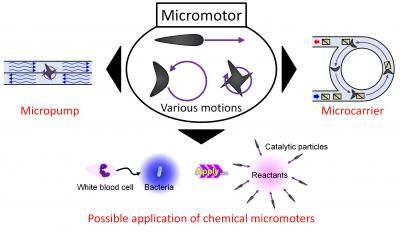
This image shows a possible application of chemical micromotors.
Daigo Yamamoto/Doshisha
Micro-sized machines operate under very different conditions than their macro-sized counterparts. The high surface-area-to-mass ratio of tiny motors means they require a constant driving force to keep them going. In the past, researchers have relied on asymmetric chemical reactions on the surface of the motors to supply the force. For example, Janus motors, are spherical particles coated with a different material on each side. One of the sides is typically made of a catalyst like platinum, which speeds up the reaction that converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. When the Janus motor is immersed in hydrogen peroxide, oxygen bubbles form more quickly on the platinum side, pushing the sphere forward.
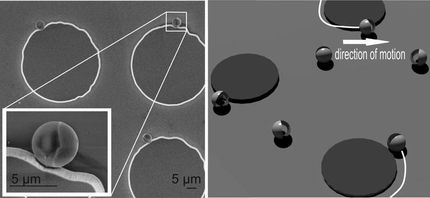
Researchers from Doshisha University in Kyoto, Japan have now discovered, however, that two-sided materials aren't necessary to make micromotors move. The researchers placed tiny spheres made only of platinum in hydrogen peroxide and observed the particles' movement through a microscope. Although the individual spheres bounced about randomly, the researchers noticed that clumps of particles began to exhibit regular motions. The clumps shaped like teardrops moved forward, those that resembled windmills started to spin, and the boomerang shaped clumps traveled in a circle. After creating a theoretical model of the forces at work, the researchers realized they could explain the regular motions by the asymmetrical drag generated by the different shapes.
The researchers envision combining their new type of motors with existing motors to create easily controllable machines with a versatile range of motions.
Micro- and nano-sized machines may one day ferry drugs around the body or help control chemical reactions, but the Japanese team also sees a more fundamental reason to study such tiny systems.
"Micromotors may be used not only as a power source for micromachines and microfactories, but may also give us significant insight regarding mysterious living phenomenon," said Daigo Yamamoto, a researcher in the Molecular Chemical Engineering Laboratory at Doshisha University and an author on the paper that describes the new motors.