Rainbows on a Nanoscale
Big impact on solar cells, television screens
Advertisement
New research at King's College London may lead to improved solar cells and LED-displays. Researchers from the Biophysics and nanotechnology Group at King's, led by Professor Anatoly Zayats in the department of physics have demonstrated in detail how to separate colours and create 'rainbows' using nanoscale structures on a metal surface. The research is published in Nature's Scientific Reports.
Researchers at King's College London discovered how to separate colors and create "rainbows" using nanoscale structures on a metal surface. This may lead to improved solar cells, TV screens and photo detectors.
Foto: Dr. Jean-Sebastien Bouillard, Dr. Ryan McCarron
More than 150 years ago, the discovery at King's of how to separate and project different colours, paved the way for modern colour televisions and displays. The major challenge for scientists in this discipline nowadays is the manipulation of colour at the nanoscale. This capability will have important implications for imaging and spectroscopy, sensing of chemical and biological agents and may lead to improved solar cells, flat-screen tv's and displays.
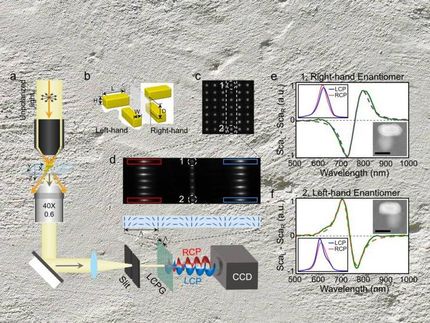
Researchers at King's were able to trap light of different colours at different positions of a nanostructured area, using especially designed nanostructures. Depending on the geometry of the nanostructure, a trapped rainbow could be created on a gold film that has the dimension on the order of a few micrometers - about 100 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
Professor Zayats explained: 'Nanostructures of various kinds are being considered for solar cell applications to boost light absorption efficiency. Our results mean that we do not need to keep solar cells illuminated at a fixed angle without compromising the efficiency of light coupling in a wide range of wavelengths. When used in reverse for screens and displays, this will lead to wider viewing angles for all possible colours.'
The big difference to natural rainbows - where red always appears on the outer side and blue on the inner side - is that in the created nanostructures the researchers were able to control where the rainbow colours would appear by controlling the nanostructures' parameters. On top of this, they discovered that it is possible to separate colours on different sides of the nanostructures.
Co-author Dr Jean-Sebastien Bouillard from King's said: 'The effects demonstrated here will be important to provide 'colour' sensitivity in infrared imaging systems for security and product control. It will also enable the construction of microscale spectrometers for sensing applications.'
The ability to couple light to nanostructures with multicolour characteristics will be of major importance for light capturing devices in a huge range of applications, from light sources, displays, photo detectors and solar cells to sensing and light manipulation in optical circuits for tele- and data communications.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!