Researchers Succeed in Realizing a New Material Class
Metafluids for Transformation Acoustics
A research team lead by Professor Martin Wegener at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) has succeeded in realizing a new material class through the manufacturing of a stable crystalline metafluid, a pentamode metamaterial. Using new nanostructuring methods, these materials can now be realized for the first time with any conceivable mechanical properties.
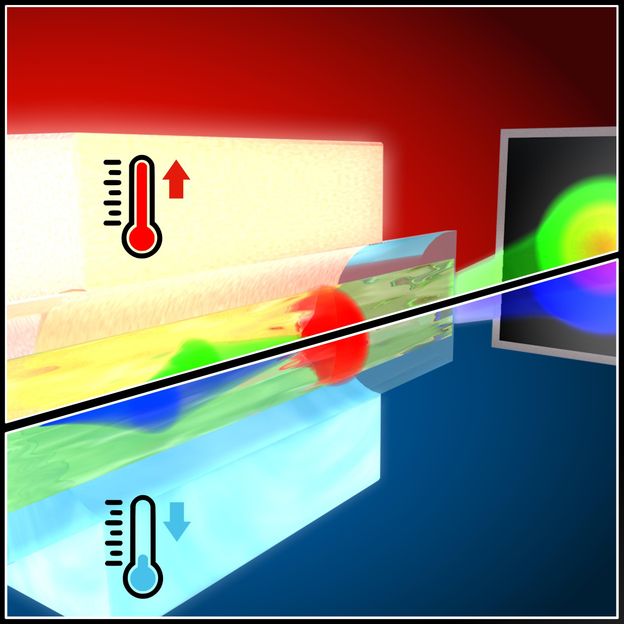
Pentamode metamaterials almost behave like fluids. Their manufacture opens new possibilities in transformation acoustics.
CFN, KIT
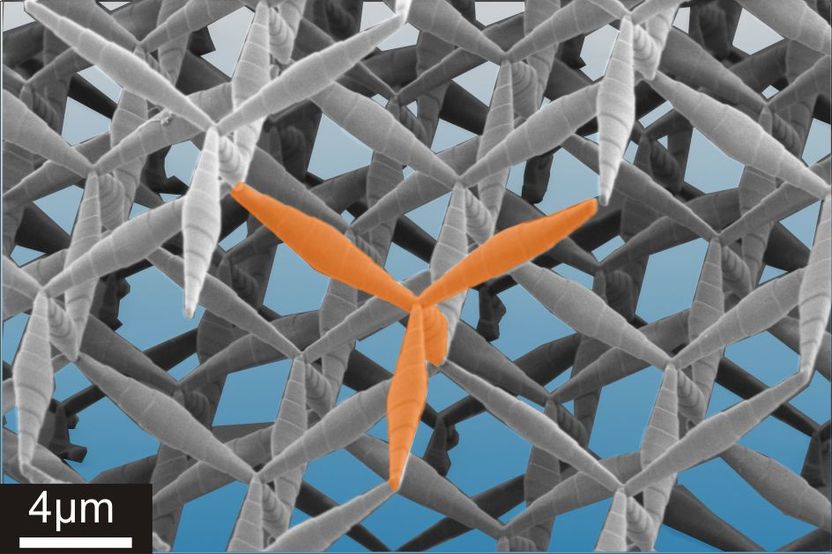
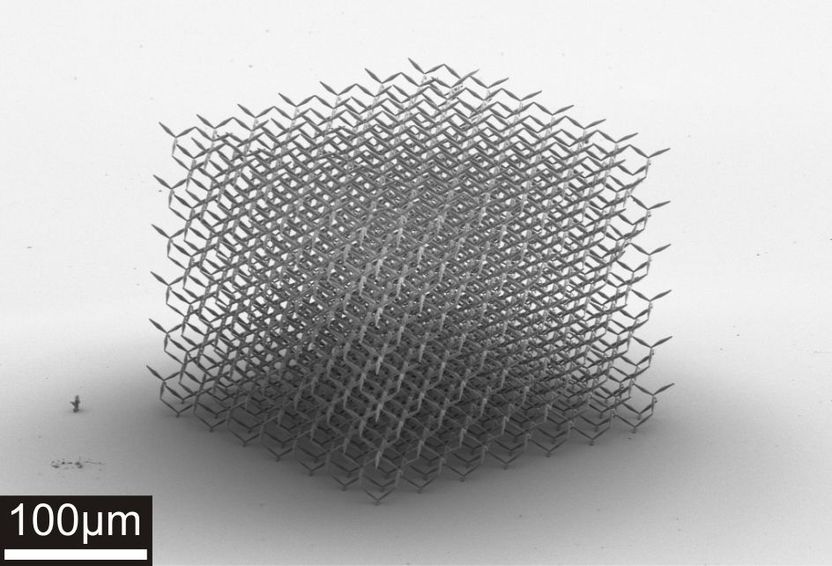
The stable four-leg structure (shown in orange) is the basic element of the pentamode metamaterial. It is arranged in the form of a three-dimensional adamantine crystal such that the resulting material as a whole can be formed.
CFN, KIT
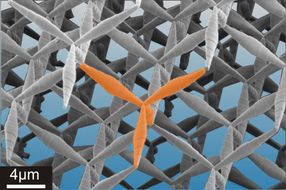
The Rubicon was crossed, so to speak, at the DFG Center for Functional Nanostructures (CFN) and at the Institute of Applied Physics (AP) in Karlsruhe during the past few months. Eventually, numerous three-dimensional transformation acoustics ideas, for example inaudibility cloaks, acoustic prisms or new loudspeaker concepts, could become reality in the near future.
So far, pentamodes, proposed in 1995 by Graeme Milton and Andrej Cherkaev, have been purely theoretical: The mechanical behavior of materials such as gold or water is expressed in terms of compression and shear parameters. Whereas the phenomenon that water, for example, can hardly be compressed in a cylinder is described through the compression parameter, the fact that it can be stirred in all directions using a spoon is expressed through the shear parameters.
The word penta is derived from ancient Greek and means “five”. In the case of water, the five shear parameters equal zero, and only one parameter, compression, differs from that value. In terms of parameters, the ideal state of a pentamode metamaterial corresponds to the state of water, which is why that material is referred to as a metafluid. Theoretically, any conceivable mechanical properties whatsoever can be obtained by varying the relevant parameters.
“Realizing a pentamode metamaterial is about as difficult as trying to build a scaffold from pins that must not touch but at their tips,” first author Dr. Muamer Kadic explains. “The Karlsruhe prototype has been manufactured from a polymer. The mechanical behavior of the material is determined by the acuteness and length of the individual “sugar loaves”. On the one hand, we must be capable of designing small sugar loaves in the nanometer range and connect them to one another at the right angle. On the other hand, the entire structure must eventually become as large as possible. Since the material itself contributes only little more than one percent to the respective volume, the composite obtained is extremely light.
“To obtain similar 3D results, as in transformation optics, transformation acoustics is exclusively dependent on metamaterials. In view of this, this first manufacture of our pentamode metamaterial is a quite significant success,” adds Tiemo Bückmann, who is about to receive his diploma at the Institute of Applied Physics and is responsible for realizing the structures of the new material by means of dip-in laser writing, a method that has been derived from direct laser writing developed by the Nanoscribe company.
In recent years, a Professor at the Institute of Applied Physics and CFN coordinator, Martin Wegener and his collaborators, have developed direct laser writing and, based on that method, established optical lithography of three-dimensional nanostructures. Numerous achievements of Wegener’s group in transformation optics e.g., the first three-dimensional cloak of invisibility in the range of visible light have been due to that technique.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Organic thin-film sensors for light-source analysis and anti-counterfeiting applications - As integrated components, the thin-film sensors could eliminate the need for external spectrometers in the future
Max_Q
Hückel_method
Shining new light on air pollutants using entangled porous frameworks
With the Technology Center, L. B. Bohle merges all steps of continuous production for the first time
Amersham Biosciences Updates Its Chromatography Handbook Reference Set - Handbooks Provide Detailed Descriptions of Common Chromatographic Techniques
MKS Instruments Reports Q2 2015 Financial Results
A Quicker Way to the Deepest Cold - New cooling procedure facilitates the realisation of quantum simulators
SciQuest Announces Agreement with Array BioPharma for New Procurement Software
Gel_point