Organic nanoelectronics a step closer
Researchers use metal crystal to organize organic materials, overcoming key stumbling block
Advertisement
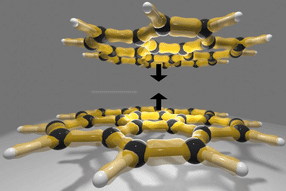
Although they could revolutionize a wide range of high-tech products such as computer displays or solar cells, organic materials do not have the same ordered chemical composition as inorganic materials, preventing scientists from using them to their full potential. But an international team of researchers led by McGill's Dr. Dmitrii Perepichka and the Institut national de la recherche scientifique's Dr. Federico Rosei have published research that shows how to solve this decades-old conundrum. The team has effectively discovered a way to order the molecules in the PEDOT, the single most industrially important conducting polymer.
Although Dr. Perepichka is quick to point out that the research is not directly applicable to products currently in the market, he gives the example of a possible use for the findings in computer chips. "It's a well known principle that the number of transistors in a computer chip doubles every two years," he said, "but we are now reaching the physical limit. By using molecular materials instead of silicon semiconductor, we could one day build transistors that are ten times smaller than what currently exists." The chips would in fact be only one molecule thick.
The technique sounds deceptively simple. The team used an inorganic material – a crystal of copper – as a template. When molecules are dropped onto the crystal, the crystal provokes a chemical reaction and creates a conducting polymer. By using a scanning probe microscope that enabled them to see surfaces with atomic resolution, the researchers discovered that the polymers had imitated the order of the crystal surface. The team is currently only able to produce the reaction in one dimension, i.e. to make a string or line of molecules. The next step will be to add a second dimension in order to make continuous sheets ("organic graphite") or electronic circuits.
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Wacker optimizes its global production network
Hydride
Michael_Heidelberger
Category:EC_3.2