“Tamed” Molecules for More Sustainable Catalysts
Successful synthesis of a spectacular gallium compound in the laboratory
catalysts play an important role in the manufacture of many products that we encounter in everyday life - for example in cars for exhaust gas purification or in the chemical industry in the production of fertilizers. Catalysts ensure that these reactions take place with low energy consumption and with as few side reactions as possible. Traditional catalysts are based on rare and hence expensive precious metals such as iridium and rhodium, which also pollute the environment. “In order to make production processes more sustainable, replacing precious metal catalysts with less toxic alternatives such as main group metals is highly desirable,” says Prof. Dr. Robert Kretschmer, Chair of Inorganic Chemistry at Chemnitz University of Technology. The use of aluminum or gallium as a substitute for precious metals has several advantages: “They are among the most abundant metals in the earth's crust, they are inexpensive and non-toxic, and they have unique chemical properties,” says the Chemnitz chemistry professor.

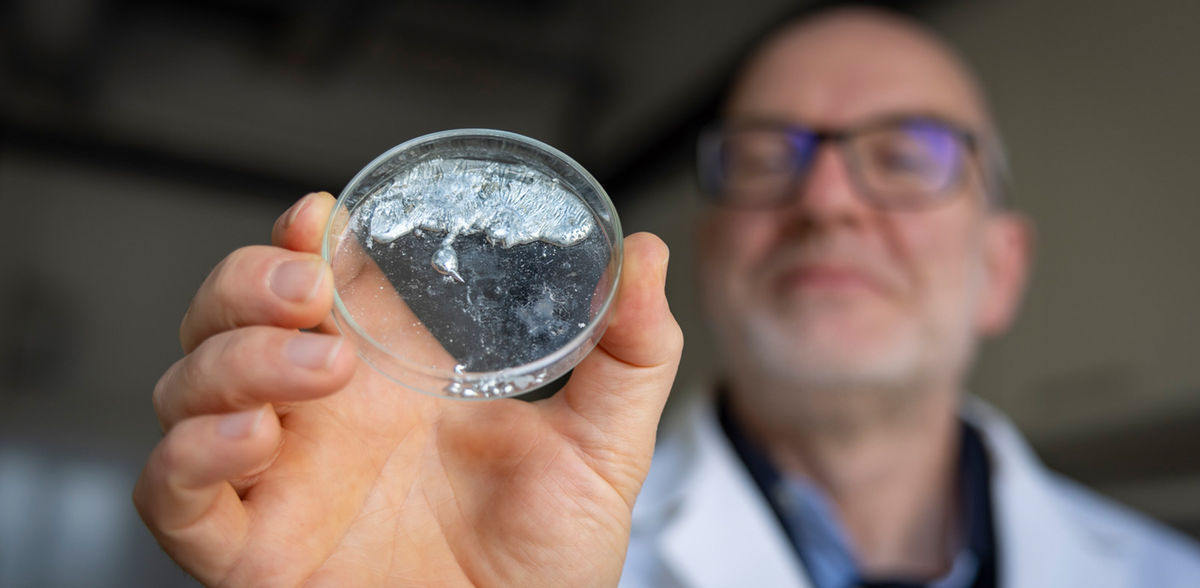
Prof. Dr. Robert Kretschmer (left) and Dr. Tobias Rüffer are part of the research team that succeeded in synthesizing an unusual compound of the metal gallium.
Jacob Müller
Unfortunately, catalytic concepts developed for precious metals cannot simply be applied to readily available elements. Therefore, the development of new methods that enable the use of for example aluminum and gallium as catalysts is a goal of global research. Chemnitz scientists from the Chair of Inorganic Chemistry have now observed for the first time a reaction of a gallium compound that was previously only known for expensive metals. “We have produced an unusual compound in which the gallium atom is only bound to a single carbon atom,” explains Kretschmer. Such compounds are very rare and there are only a few research groups in the world that are able to “tame” such molecules in the laboratory.
The reactivity of the new compound is particularly spectacular: “While gallium normally strives to increase the number of bonds in a reaction, our team has now succeeded for the first time in a reaction in which the metal only has one bond at the end – but the gallium atom has jumped two carbon atoms further,” says Kretschmer. Such so-called insertion reactions play an important role in a large number of industrial syntheses and the observation now opens up perspectives for the further development of catalysis.
The Chemnitz research results were published in the renowned journal “Nature Synthesis” in September 2024. Due to the high relevance of the work, it was also honored with a report in “Nature Briefing”.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.