Adhesive Comes Unglued on Command
Oxidation triggers debonding of mussel-inspired adhesive
Advertisement
Modern integrated microelectronic devices are often poorly repairable and difficult to recycle. Debondable adhesives play a key role in the transition to a circular economy with sustainable resources, less waste, and intelligent repair/recycling strategies. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a research team has now introduced a method for making adhesives that can be deactivated “on command”.
© Wiley-VCH
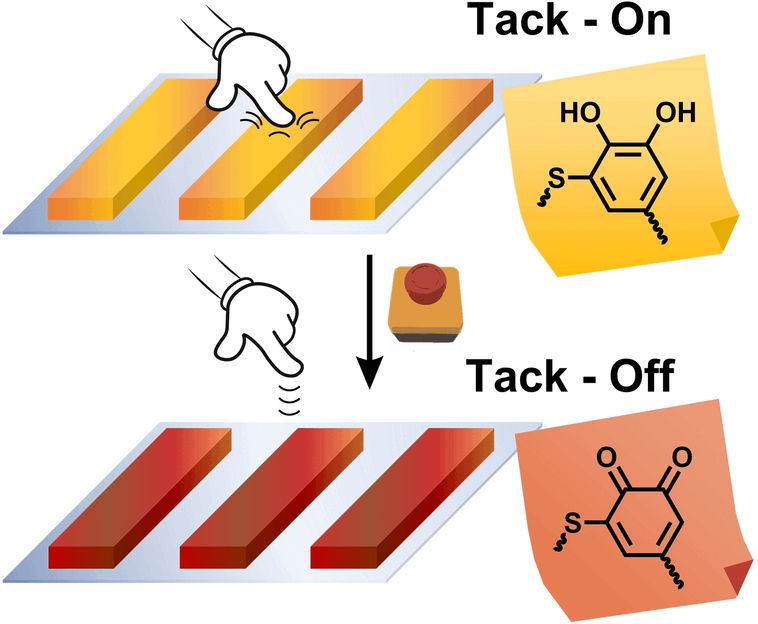
Their inspiration came from the masters of underwater adhesion: mussels. Mussel-inspired adhesives have been developed before. These new versions are based on thiol-catechol polyaddition, which forms polymers with adhesive thiol-catechol connectivities (TCC, thiol-substituted six-membered aromatic rings with two neighboring OH groups which are responsible for the strong adhesive properties). The trick is that when the catechol groups in the adhesive polymers are oxidized to quinones (six-membered rings with two oxygen atoms bound by double bonds), the strength of adhesion decreases dramatically.
Changing the basic framework of the monomers allows for control over the properties of the polymers. Kannan Balasubramanian, Hans Börner, and their team at Humboldt University zu Berlin, the Leibniz Institute for Analytical Sciences (ISAS, Berlin, Germany), Universidad Nacional de General San Martin (Buenos Aires, Argentina), the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research (Potsdam-Golm, Germany), and the company Henkel (Düsseldorf, Germany) have now produced two different types of TCC adhesives with strong adhesion and shear strength.
Biobased, peptidic biscatechol precursors of DiDOPA, which is similarly found in mussels, were compared with their fossil-based analog. Both adhesives also function under water and are insensitive to atmospheric oxygen and weak oxidizing agents. However, they lose their stickiness through oxidation with the strongly oxidizing sodium periodate (NaIO4), so that the adhesive residues can be easily peeled or wiped off the substrate in one piece.
While the oxidation of the fossil adhesive inactivates the catechols, but at the same time makes the adhesive more hydrophobic, the biobased type shows the deactivation without becoming dramatically more hydrophobic due to a variety of other peptide functionalities. Börner explains: "The multifunctionality is typical of biomaterials, in which often only the key functionalities are switched off and not much else changes in the material. This circumstance enables a dramatically more efficient de-adhesion mechanism, which reduces the adhesive strength of the bio-based type by 99%." The reason for the poorer deactivation (60%) of the fossil-based adhesive lies in the compensation, as hydrophobic polymers are also very good adhesives.
In the longer term, the consortium is working on replacing chemical oxidation with direct electrochemical oxidation, which could be interesting for the repair of cell phones, for example.
Original publication
Tilmann J. Neubert, Keven Walter, Carolin Schröter, Victoria Guglielmotti, Karsten Hinrichs, Stefan Reinicke, Andreas Taden, Kannan Balasubramanian, Hans G. Börner; "Redox‐Triggered Debonding of Mussel‐Inspired Pressure Sensitive Adhesives: Improving Efficiency Through Functional Design"; Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024-9-17