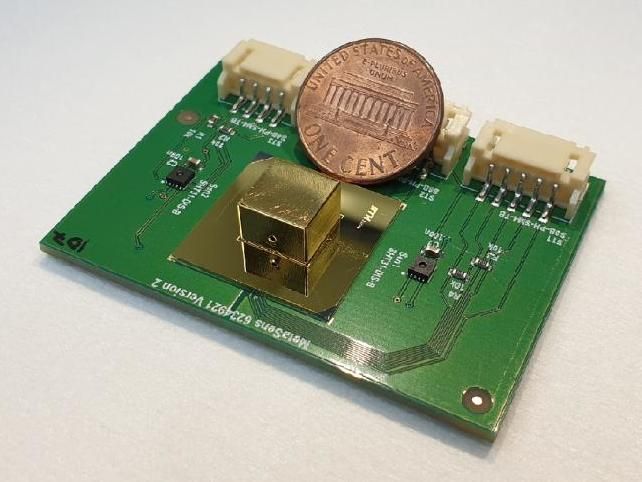
Pocket-sized invention revolutionizes ability to detect harmful materials
The low-cost cellphone-based Raman spectrometer system can make identifications of unknown biological molecules within minutes
Imagine knowing what berry or mushroom is safe to eat during a hike or swiftly detecting pathogens in a hospital setting that would traditionally require days to identify.

A smartphone records the Raman spectrum of an unknown material (an ethanol solution, in this case) for further analysis.
Texas A&M University Engineering
Identification and detection of drugs, chemicals and biological molecules invisible to the human eye can be made possible through the combined technology of a cellphone camera and a Raman spectrometer — a powerful laser chemical analysis method.
Dr. Peter Rentzepis, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Texas A&M University, holds a patent for a hand-held cellphone-based Raman spectrometer system. Rentzepis’ invention allows the user to make non-invasive identifications of potentially harmful chemicals or materials in the field, especially in remote areas where laboratory spectrometers cannot be used due to their size and power needs.
This new Raman spectrometer system integrates lenses, a diode laser and a diffraction grating — a small thin square-shaped surface that scatters light for analysis — in combination with a camera from a cellphone to record the Raman spectrum. Peaks in the spectrum provide detailed data about the chemical composition and molecular structure of a substance, depending on their intensities and positions.
To use the device, a cellphone is placed behind the transmission grating with the camera facing the grating, ready to record the Raman spectrum. A laser shoots a beam into a sample of unknown material, such as a bacterium, on a slide. The camera records the spectrum, and when paired with an appropriate cellphone application/database, this handheld instrument can enable rapid materials identification on site.
Previously, the process of identifying unknown substances involved extensive sampling of biological material and laboratory analysis, which could take several hours or even days. While traditional Raman spectrometers cost up to thousands of dollars, Rentzepis’ invention can be made at a significantly lower cost and can identify materials at a significantly quicker speed.
“It’s a small device that can tell you the composition of a particular system, material or sample,” Rentzepis said. “You can even have it in your pocket.”
Fellow inventors are former graduate students Dr. Dinesh Dhankhar, a system engineer at Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Anushka Nagpal, a process engineer at Intel Corporation.
Funding for this research is administered by the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station (TEES), the official research agency for Texas A&M Engineering.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

MIRA P Basic by Metrohm
Identify raw materials immediately - without waiting time
State-of-the-art Raman technology in a compact device
i-Raman Prime 785S by Metrohm
Mobile Raman spectrometer for real-time data analysis on site
Maximum performance, minimum effort - Raman measurements made easy

ReactRaman™ 802L by Mettler-Toledo
ReactRaman in-situ-Measurement of Reaction and Process Trends in Real Time
Raman - Specific Information on Kinetics, Polymorphic Transitions and Critical Process Parameters
2060 Raman Analyzer by Metrohm
Self-calibrating inline Raman spectrometer
Analyze solids, liquids and gases - for reproducible, accurate results in the process

2060 Raman Analyzer by Metrohm
Revolutionize your production: real-time Raman analysis for maximum efficiency
Self-monitoring high-throughput spectrometer: efficient process control in any process environment
alphaCART by WITec
Mobile Raman microspectroscopy: laboratory analysis directly on the object
Non-destructive analysis of large, immobile samples that do not fit under a microscope

LabRAM Soleil by Horiba
The fastest automated Raman imaging microscope
Highest light throughput, precision, automation and intelligent software for high-speed-imaging

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Photometry
Photometry, the measurement of light intensity in relation to interaction with molecules, is a key tool in chemistry and life sciences. It enables researchers to determine concentrations of substances in solutions, follow reaction kinetics or check the quality of samples and provides valuable data for analyses, from quality control in the laboratory to clinical diagnostics.

Topic world Photometry
Photometry, the measurement of light intensity in relation to interaction with molecules, is a key tool in chemistry and life sciences. It enables researchers to determine concentrations of substances in solutions, follow reaction kinetics or check the quality of samples and provides valuable data for analyses, from quality control in the laboratory to clinical diagnostics.
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!