How lab-made catalysts can help to get a grip on difficult greenhouse gases
natural gas consists of light hydrocarbons such as methane and ethane. Such gases are more potent Greenhouse Gases than CO2, are constantly released into the atmosphere from natural gas wells, and are more difficult to store than, for example, their corresponding alcohols (methanol and ethanol, respectively). While large scale facilities exist for such transformations, the excessive cost of building and operating such plants at smaller natural gas wells precludes effective conversion globally. Thus, new cost-effective and benign technologies to solve this problem are highly sought after. The direct Oxidation of hydrocarbon constituents of natural gas with abundant O2 as the oxidant at near ambient temperatures and pressure is therefore extremely attractive for the development of new green technologies for hydrocarbon valorization.
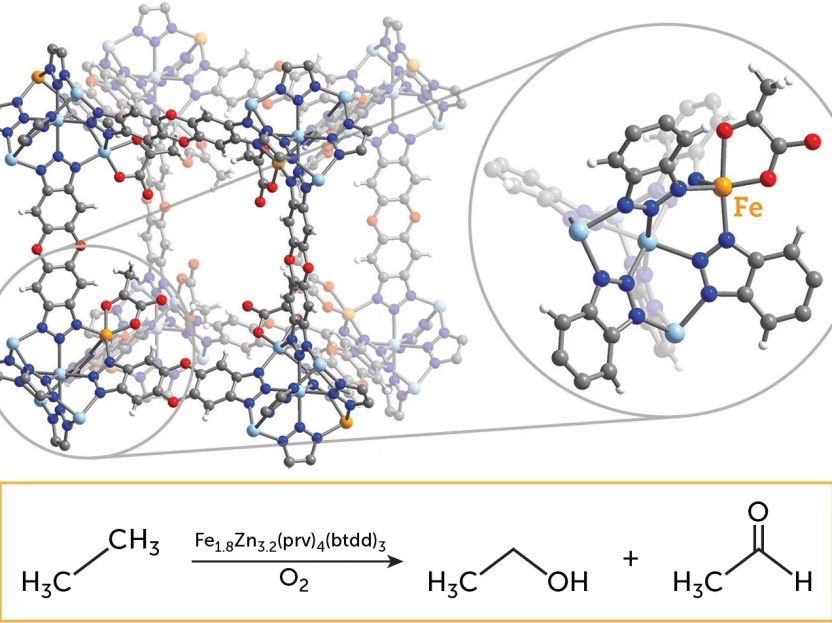
The figure depicts a cubic pore of the novel metal-organic framework (MOF) that was designed to mimic the enzyme taurine–α-ketoglutarate dioxygenase. The inset focuses on a cluster node of the MOF, showing the local iron site environment. The figure also shows one of the important reactions investigated in the paper, the oxidation of ethane to ethanol and acetaldehyde.
Dimitrios Pantazis/Max Planck Chemistry Campus Mülheim
Nature has developed enzymes that are capable of activating dioxygen for selective hydrocarbon oxygenation reactions. One class of non-heme iron containing enzymes is the α-ketoglutarate dependent dioxygenases such as the well-studied enzyme taurine dioxygenase (TauD). This enzyme utilizes an α-keto acid as a co-substrate to cleave the oxygen-oxygen bond of dioxygen to yield a reactive iron-oxo species (TauD-J) that oxygenates abundant C–H bonds directly to provide the corresponding alcohols.
An international team of researchers led by Prof. Jeffrey R. Long at UC Berkeley, including researchers from both Mülheim Max Planck Institutes (MPI für Kohlenforschung and MPI for Chemical Energy Conversion): directors Frank Neese and Serena DeBeer, as well as group leaders Eckhard Bill (deceased October 6th, 2022), Daniel J. SantaLucia, Dimitrios A. Pantazis, and Sergey Peredkov, was able to mimic the TauD functionality in a heterogenous catalyst material that is well-suited for solid-gas reactions. This material belongs to the class of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are crystalline porous materials consisting of organic linkers and metal ions or cluster nodes that feature large surface areas. The structures are highly chemically tunable, and thus allow for well-defined tailoring of new heterogeneous catalysts.
The new materials are capable of catalytic hydrocarbon oxygenation at near ambient temperatures utilizing O2—reminiscent of enzyme reactivity. The team at the Mülheim Chemistry Campus studied the reactive intermediate generated from the starting MOF and O2, a high-valent iron-oxo species. The nature of the material allowed for site-isolation of this reactive iron-oxo species, which was studied with various state-of-the-art spectroscopic techniques, namely variable-temperature variable-field Mössbauer spectroscopy and Fe Kβ X-ray emission spectroscopy (collected at the PINK X-ray beamline at BESSY II at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie), as well as state-of-the-art computational methods, which confirmed structural and electronic similarities with TauD-J, namely that the intermediate is in a high-spin state. Significantly, this is the first non-enzymatic system that oxidizes light hydrocarbons with dioxygen akin to metalloenzyme reactivity via a fully characterized high-spin iron-oxo intermediate.
Original publication
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!



























































