Carrots: Good for your eyes … and for degradable polymers
Researchers have incorporated a compound derived from β-carotene into a polymer that’s fully degradable
Advertisement
Carrots come in a rainbow of bright colors — red, orange, yellow and purplish black — because of compounds called carotenoids. They help support eye health by reacting with potentially harmful UV light. Interestingly, the molecular structures of carotenoids, such as β-carotene, are similar to the building blocks of some polymers. Now, researchers reporting in the Journal of the American Chemical Society have incorporated a compound derived from β-carotene into a polymer that’s fully degradable.
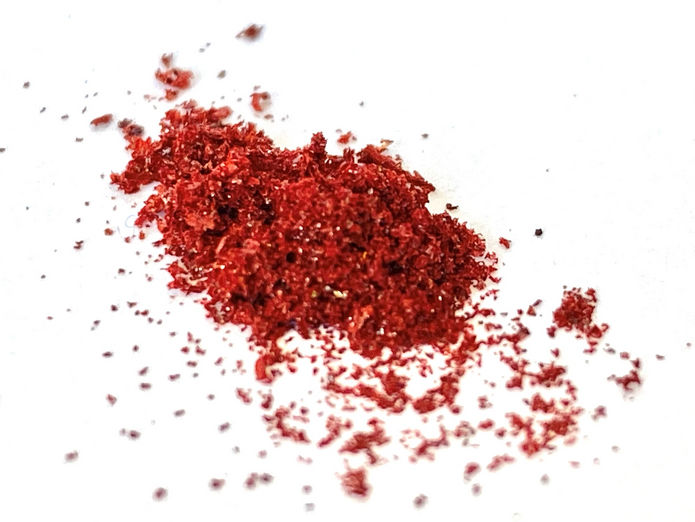

A compound derived from β-carotene was one of the building blocks in a fully degradable, biobased polymer.
Helen Tran
Polymers and plastics formed from natural, biodegradable ingredients are highly desired for use in consumer products. By using indigo, vanillin and melanin, scientists have created biobased polymers that have electrically conductive properties that are attractive for energy storage, biomedical and sensor applications. Carotenoids are another set of natural compounds expected to transfer charges, but they haven’t been widely tested in polymer design. Another possible benefit is that these compounds break apart in the presence of UV light and certain chemicals. So, Azalea Uva, Angela Lin and Helen Tran wanted to use a carotenoid-sourced compound to make a degradable material that could be selectively broken down with an acid and sunlight.
The researchers combined the carotenoid derived from β-carotene, a 10-carbon dialdehyde, and p-phenylenediamines, a group of compounds used in degradable polymers, to make three different poly(azomethine)s. When dried, the resulting materials ranged in color from black to bright red.
In initial experiments, the team determined that the bright red version — created with p-phenylenediamine containing two hexyl side chains — was the best candidate to test further. The material completely broke down into its original components in acidic solutions, which could potentially be recovered. However, when both acid and artificial sunlight were used, this process sped up. And after an extended period of time, the sample broke down even further into smaller dialdehydes and other compounds. The next step is to evaluate this new fully degradable polymer’s ability to conduct electricity, the researchers say.