Adventures in nanotech: growing a nano particle metallic snowflake
Scientists working at the level of atoms are manipulating metals, opening up possibilities for creating new materials
Scientists in New Zealand and Australia working at the level of atoms created something unexpected: tiny metallic snowflakes. Why’s that significant? Because coaxing individual atoms to cooperate in desired ways is leading to a revolution in engineering and technology via nanomaterials (And creating snowflakes is cool.) Nanoscale structures (a nanometre is one billionth of a metre) can aid electronic manufacturing, make materials stronger yet lighter, or aid environmental clean-ups by binding to toxins.
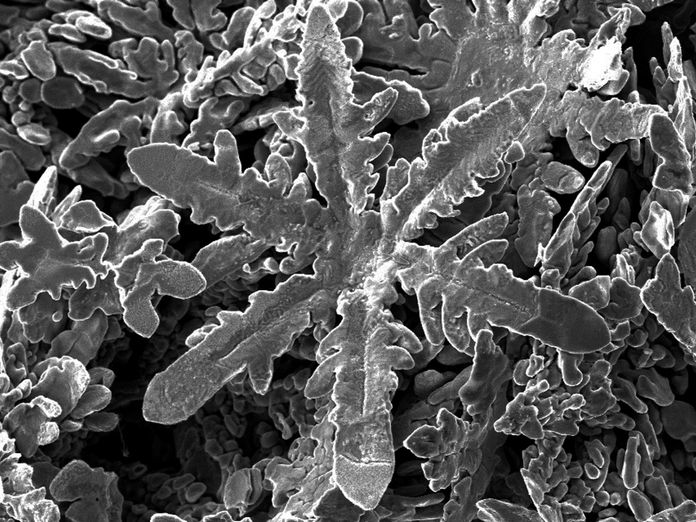

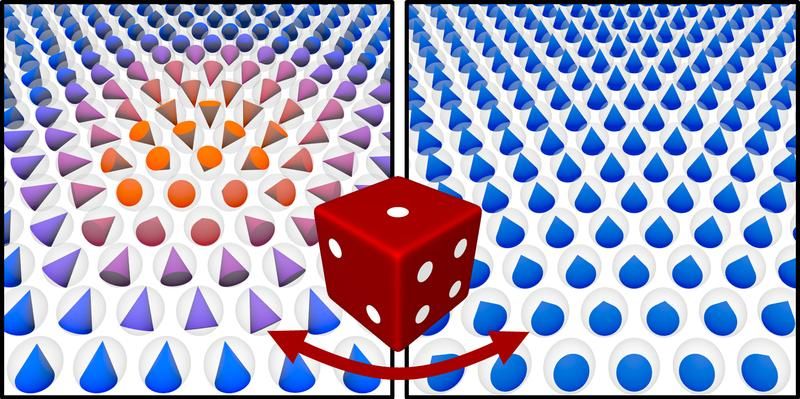
Nano-scale snowflake from Gallium solvent
Waipapa Taumata Rau, University of Auckland
To create metallic nanocrystals, New Zealand and Australian scientists have been experimenting with gallium, a soft, silvery metal which is used in semiconductors and, unusually, liquifies at just above room temperature. Their results were just reported in the journal Science.
Professor Nicola Gaston and research fellow Dr Steph Lambie, both of Waipapa Taumata Rau, University of Auckland, and Dr Krista Steenbergen of Te Herenga Waka, Victoria University of Wellington, collaborated with colleagues in Australia led by Professor Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh at the University of New South Wales.
The Australian team worked in the lab with nickel, copper, zinc, tin, platinum, bismuth, silver and aluminium, growing metal crystals in a liquid solvent of gallium. Metals were dissolved in gallium at high temperatures. Once cooled, the metallic crystals emerged while the gallium remained liquid. The New Zealand team, part of the MacDiarmid Institute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology, a national Centre of Research Excellence, carried out simulations of molecular dynamics to explain why differently shaped crystals emerge from different metals. (The government’s Marsden Fund supported the research.)
“What we are learning is that the structure of the liquid gallium is very important,” says Gaston. “That’s novel because we usually think of liquids as lacking structure or being only randomly structured.” Interactions between the atomistic structures of the different metals and the liquid gallium cause differently shaped crystals to emerge, the scientists showed.
The crystals included cubes, rods, hexagonal plates and the zinc snowflake shapes. The six-branched symmetry of zinc, with each atom surrounded by six neighbours at equivalent distances, accounts for the snowflake design. “In contrast to top-down approaches to forming nanostructure – by cutting away material – this bottom-up approaches relies on atoms self-assembling,” says Gaston. “This is how nature makes nanoparticles, and is both less wasteful and much more precise than top-down methods.” She says the research has opened up a new, unexplored pathway for metallic nanostructures. “There’s also something very cool in creating a metallic snowflake!”
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
MODTRAN
Fiorinal
Citgo
Galenic_formulation
Fluoride_volatility
Category:Titanium_minerals
Kenmare_Resources
Foundation_for_Focused_Ultrasound_Research
Boron can form a purely honeycomb, graphene-like 2-D structure
Acacia_concinna
Teratology