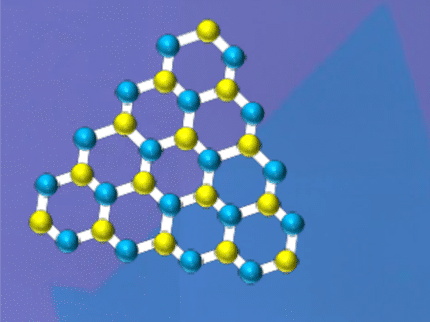
Bioinspired protein creates stretchable 2D layered materials
Nature creates layered materials like bone and mother-of-pearl that become less sensitive to defects as they grow. Now researchers have created, using biomimetic proteins patterned on squid ring teeth, composite layered 2D materials that are resistant to breaking and extremely stretchable.
Using biomimetic proteins patterned on squid ring teeth, researchers have created composite layered 2D materials that are resistant to breaking and extremely stretchable.
Burcu Dursun, Penn State
"Researchers rarely reported this interface property for the bone and nacre because it was difficult to measure experimentally," said Melik Demirel, Lloyd and Dorothy Foehr Huck Chair in Biomimetic Materials and director of the Center for Advanced Fiber Technologies, Penn State.
Composite 2D materials are made up of atom-thick layers of a hard material, like graphene or a MXene — usually a transition metal carbide, nitride or carbonitride — separated by layers of something to glue the layers together. While large chunks of graphene or MXenes have bulk properties, 2D composites' strength comes from interfacial properties.
"Because we are using an interfacial material that we can modify by repeating sequences, we can fine tune the properties," said Demirel. "We can make it very flexible and very strong at the same time."
He noted that the materials can also have unique thermal conduction regimes, or properties, spreading heat in one direction more strongly than at 90 degrees. The results of this work were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"This material would be great for insoles for running shoes," said Demirel. "It could cool the foot and the repeated flexing would not break the insole."
These 2D composites could be used for flexible circuit boards, wearable devices and other equipment that requires strength and flexibility.
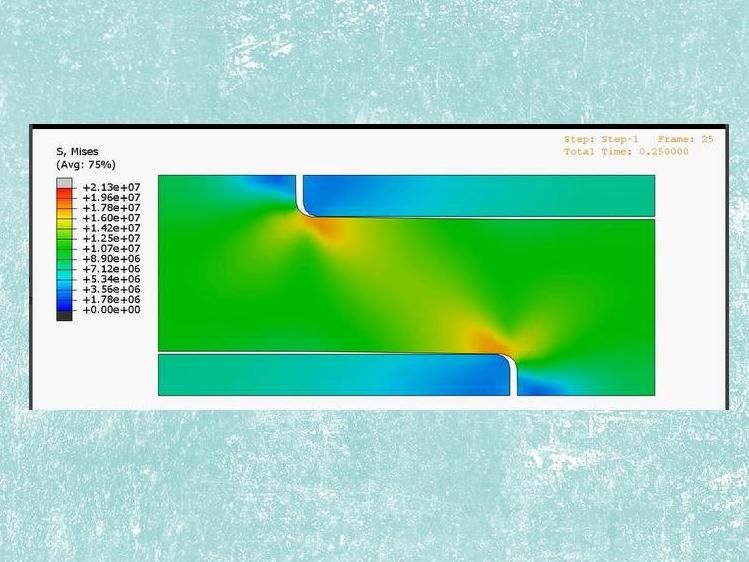
According to Demirel, traditional continuum theory does not explain why these materials are both strong and flexible, but simulations demonstrated that the interface matters. What apparently happens is that with a higher percent of the material composed of the interface, the interface breaks in places when the material is under stress, but the material as a whole does not break.
"The interface breaks, but the material doesn't," said Demirel. "We expected them to become compliant, but all of a sudden it is not only compliant, but super stretchy."
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Molecule as supplier and energy storage solution for solar energy - “Our new approach involves controlling the process to allow the stored energy to be made available as electricity as well, even after months have passed”
Chemical trickery corrals 'hyperactive' metal-oxide cluster
Radleys Discovery Technologies increases focus on the US market