A better wig — with chemistry
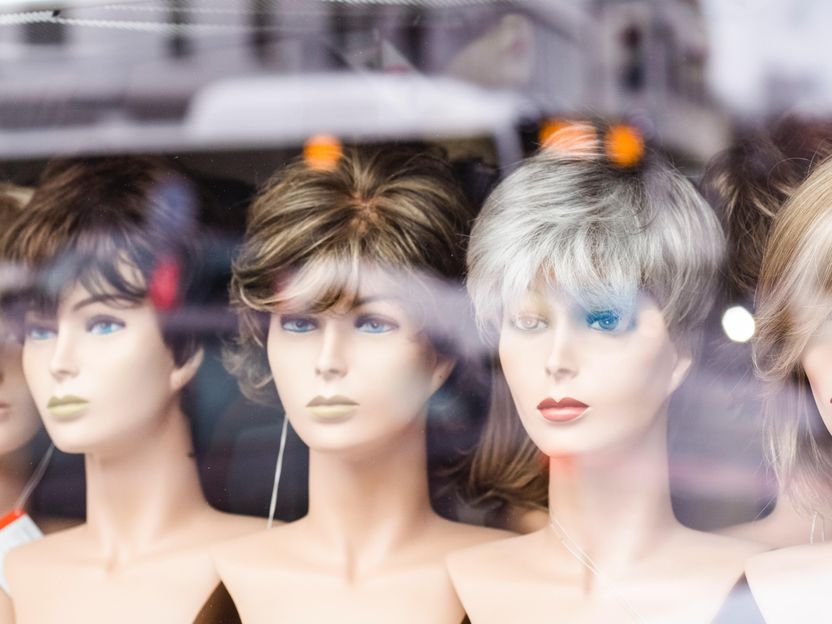
Hairs coated with a nanocomposite using the Langmuir-Blodgett technique generate much less static electricity than untreated hairs
For some people, wigs are a fun and colorful fashion accessory, but for those with hair loss from alopecia or other conditions, they can provide a real sense of normalcy and boost self-confidence. Whether made from human or synthetic strands, however, most hairpieces lose their luster after being worn day after day. Now, researchers in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces report a new way to make wigs more durable and long lasting.

Symbolic image
Unsplash

Hairs coated with a nanocomposite (left) using the Langmuir-Blodgett technique generate much less static electricity than untreated hairs (right).
Adapted from ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2022, DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c05965


Wigs come in all colors of the rainbow and in every style imaginable. Some cover the whole head, while others are “extensions,” sections of hair that clip onto existing locks to make them look fuller or longer. Hairpieces can be made of real human strands or synthetic materials, but either way, washing, UV exposure from the sun and repeated styling can cause these products to become dry and brittle. To extend the wearable life of wigs, some researchers have spray-coated a layer of graphene oxide on them, whereas other teams have immersed wig hairs in a keratin/halloysite nanocomposite. Because it’s difficult to cover an entire hairpiece with these methods, Guang Yang, Huali Nie and colleagues wanted to see if a nanocomposite applied with a tried-and-true approach for coating surfaces with ultrathin films — known as the Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) technique — could improve coverage and increase durability.
The researchers first developed a keratin and graphene oxide nanocomposite as the coating material. To coat hairs with the LB method, they dipped a few human or synthetic hairs into water in a special apparatus with moveable side barriers. After the nanocomposite was spread on the water’s surface with an atomizer, the barriers were moved inward to compress the film— like the trash compactor that almost crushed the heroes in the movie Star Wars. After 30 minutes, the researchers lifted the hairs out of the water, and as they did so, the film coated the locks.
Compared to the immersion technique, the LB method provided more coverage. In addition, hairs treated with the LB approach sustained less UV damage, were less prone to breakage and could hold more moisture than those that were simply immersed in the nanocomposite. They also dissipated heat better and generated less static electricity when rubbed with a rubber sheet. The researchers say that the method can be scaled up for use by companies that manufacture wigs.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
OCA 200 by DataPhysics
Using contact angle meter to comprehensively characterise wetting behaviour, solids, and liquids
With its intuitive software and as a modular system, the OCA 200 answers to all customers’ needs

Tailor-made products for specific applications by IPC Process Center
Granulates and pellets - we develop and manufacture the perfect solution for you
Agglomeration of powders, pelletising of powders and fluids, coating with melts and polymers
Dursan by SilcoTek
Innovative coating revolutionizes LC analysis
Stainless steel components with the performance of PEEK - inert, robust and cost-effective

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.





























































