Breakthrough in synthesis chemistry: Chemists use light energy to produce small molecular rings
New synthesis route for producing sensitive molecules under mild reaction conditions
In the search for new active agents in medicine, molecules whose atoms are linked in rings are becoming increasingly important. Such ring systems have particularly suitable properties for producing such active agents and they are driving the development of innovative treatments for malignant tumours, as well as for neurodegenerative and infectious diseases. A team of chemists headed by Prof. Frank Glorius from the University of Münster has now succeeded in synthesising new and medically significant small molecular rings, which are difficult to produce because they are particularly sensitive. The team’s work has been published in the journal “Nature Catalysis”.
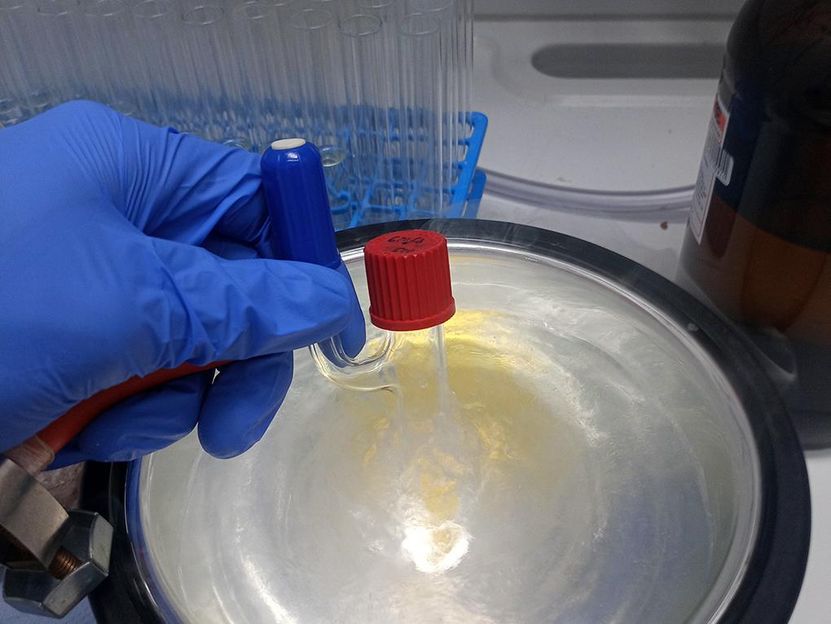

The reaction mixture is frozen using liquid nitrogen, in order to replace the oxygen-containing atmosphere with inert nobel gas argon.
© University of Münster - Peter Bellotti
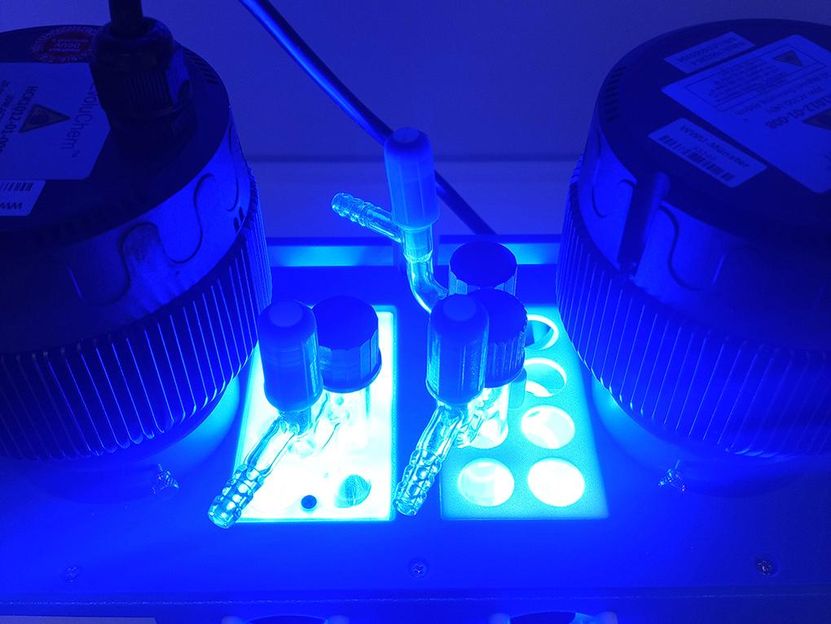

The reaction is irradiated with blue light generated with high-power LEDs for the cycloaddition process to proceed.
© University of Münster – Peter Bellotti


Among chemists, especially the synthesis of small ring systems from so-called aromatic compounds is considered to be difficult. Also, an especially large amount of energy is needed for the process. A further hurdle is that the energy has to be released selectively to the source materials, but not to the heat-sensitive products. Frank Glorius’ team has now developed a strategy in which visible light, as an inexpensive energy source, activates a photocatalyst which drives the reaction. The photocatalyst absorbs the light and transfers its energy to the source materials. In this way, it enables synthesis to take place which is highly efficient and mild and which has no, or hardly any, undesired side-reactions.
“We see our study as a breakthrough in synthesis chemistry,” says lead author Dr. Jiajia Ma. “It shows that light energy can be used in a targeted way to produce small ring systems. The fact that, by using different reaction partners, we can produce different ring systems provides numerous opportunities for the production of active agents.” For their source materials, the chemists used only easily available, inexpensive raw materials.
The study was produced in collaboration with Prof. Kendall Houk, from the University of California in Los Angeles (USA), who is recognised worldwide as an expert on computer chemistry. Houk’s computer calculations were done with Shuming Chen, a Professor at the elite American undergraduate institution, Oberlin College (Ohio). Working together, the researchers succeeded in explaining the underlying reaction mechanism.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.