Microalgae-based conversion of carbon dioxide to biofuels
Scientists explore a genetic sensor of blue light to double oil productivity in industrial microalgae
microalgae, algae that cannot be seen by the naked eye, absorb carbon dioxide and produce oils that can be used as biofuels. These biofuels, which can be carbon negative, offer promise as an alternative to conventional fossil fuels. However, the biological processes that allow these microalgae to produce oils are not fully understood.
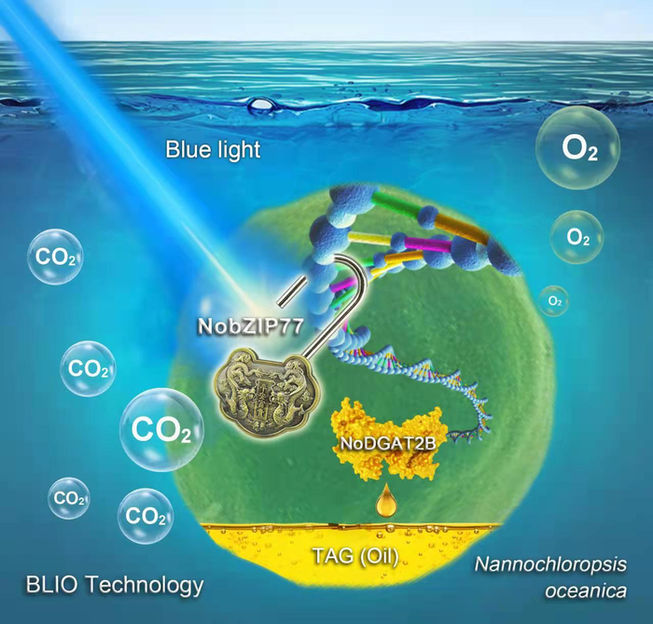
The BLIO technology explores a "genetic switch" to unlock oil production in microalgae
LIU Yang and ZHANG Peng
Now, a research team led by Prof. XU Jian from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has discovered a genetic sensor of blue light that regulates oil synthesis in an industrial microalga, and explored this discovery to double the microalgal productivity of oils.
They proposed a new technology called Blue-Light Induced Oil synthesis (BLIO), which has major implications in microalgae-based conversion of carbon dioxide to biofuels. Their findings were published on March 29 in Nature Communications.
In the oil-producing algae, called oleaginous microalgae, environmental stresses such as nutrient deprivation, high light or heat typically cause the oil to accumulate. These high energy density oils are triacylglycerols (TAGs), precursors for biodiesels. Microalgae are promising feedstock for TAG production due to their rapid growth and high oil contents.
Scientists have long known that oil production is part of the response of microalgal cells to environmental stresses, but exploiting this knowledge for greater oil productivity is hard because they lack a full understanding of how the process works.
The QIBEBT research team has long been looking for a better way to induce the oil productivity in microalgae. "New environmental stimuli that allow efficient and precise control of cellular TAG assembly yet without compromising biomass productivity are highly desirable," said ZHANG Peng, a postdoctoral researcher at Single-Cell Center of QIBEBT.
The team has been studying the industrial oleaginous microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica, a type of marine microalgae that can produce high-value oils from sea water and CO2, for over a decade.
Their long journey to search for a new stimulus that they can control more precisely for oil production eventually led them to blue light. The research team discovered a previously unknown "BlueLight-NobZIP77-NoDGAT2B" pathway.
When nutrients such as nitrogen are abundant, a blue-light-sensing regulator called NobZIP77 would turn off TAG production in the microalga, by inhibiting the expression of oil-producing enzymes such as NoDGAT2B. "However, when nitrogen is depleted, chlorophyll a which normally absorbs blue light is reduced, resulting in more blue light entering the nucleus where NobZIP77 resides in. The increased exposure of NobZIP77 to blue light unlocks its inhibiting effect on TAG-synthetic enzymes, and unleashes NoDGAT2B to produce more TAGs." ZHANG Peng explained.
"Such a concise mechanism that links light sensing to TAG synthesis was not previously known, thus is quite exciting," added XIN Yi, an associate professor at Single-Cell Center.
Based on these findings, the team invented BLIO technology, in which the NobZIP77-removed microalga is first exposed to white light and then to blue light. This results in a level of peak productivity of TAG that is double of the unmodified microalga under constant white light.
"Light quality is a highly desirable tool of control. Thus, our discovery in this study points to a new direction in feedstock development, photobioreactor design, or bioprocess control," said XU Jian, Head of Single-Cell Center and the senior author of the study.
The researchers believe this genetic mechanism is widely present in microalgae and higher plants, and envision a future when the BLIO technology and its variants contribute to circumstances where highly efficient conversion of CO2 to oils or other macromolecules is required.