Impossible material made possible inside a graphene sandwich
Towards new 2D materials
Advertisement
Atoms bind together by sharing electrons. The way this happens depends on the atom types but also on conditions such as temperature and pressure. In two-dimensional (2D) materials, such as graphene, atoms join along a plane to form structures just one atom thick, which leads to fascinating properties determined by quantum mechanics. Researchers at the University of Vienna in collaboration with the Universities of Tübingen, Antwerp and CY Cergy Paris, together with Danubia NanoTech, have produced a new 2D material made of copper and iodine atoms sandwiched between two graphene sheets.
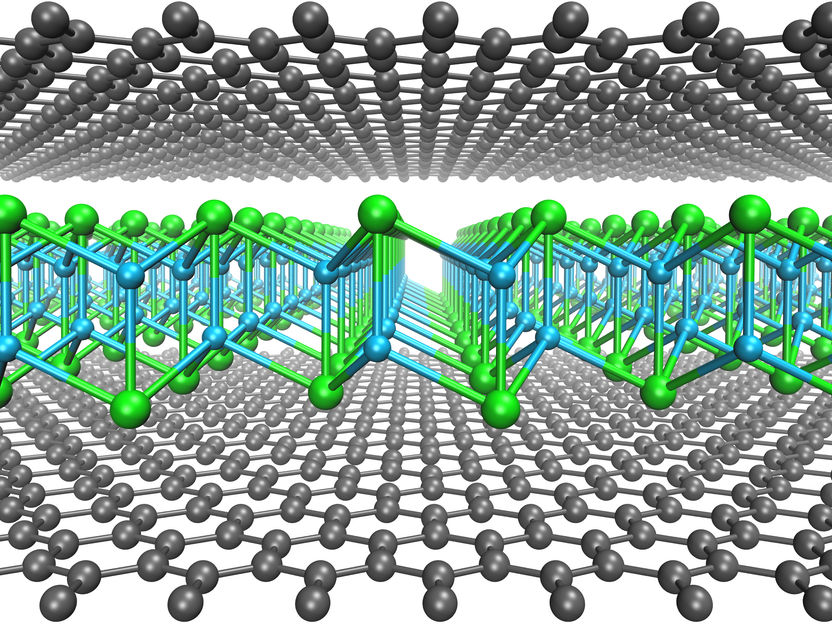
A single layer of cuprous iodide encapsulated in between two sheets of graphene (gray atoms).
©2021 Kimmo Mustonen, Christoph Hofer und Viera Skákalová
The design of new materials allows for either improved efficiency of known applications or totally new applications that were out of reach with the previously existing materials. Indeed, tens of thousands of conventional materials such as metals and their alloys have been identified over the last hundred years. A similar number of possible 2D materials have been predicted to exist, but as of now, only a fraction of them have been produced in experiments. One reason for this is the instability of many of these materials in laboratory conditions.
In the recent study, the researchers synthesized 2D cuprous iodide that was stabilized in a graphene sandwich, as the first example of a material that does not otherwise exist in normal laboratory conditions. The synthesis utilizes the large interlayer spacing of oxidized graphene multilayers, which allows iodine and copper atoms to diffuse into the gap and to grow the new material. The graphene layers here have an important role imposing a high pressure on the sandwiched material that thus becomes stabilized. The resulting sandwich structure is shown in the illustration.
"As so often, when we first saw the new material in our microscopy images, it was a surprise", says Kimmo Mustonen, the lead author of the study. "It took us quite some time to figure out what the structure precisely was. This enabled us together with Danubia NanoTech company, headed by Viera Skákalová, to design a chemical process for producing it in large scale", he continues. Understanding the structure was a joint effort of scientists from the Universities of Vienna, Tübingen, Antwerp and CY Cergy Paris. "We had to use several electron microscopy techniques to make sure that we were really seeing a monolayer of copper and iodine and to extract the exact atom positions in 3D, including the latest methods we have recently developed", the second lead author Christoph Hofer adds.
Following the 2D copper iodide, the researchers have already expanded the synthesis method to produce other new 2D materials. "The method seems to be truly universal, providing access to dozens of new 2D materials. These are truly exciting times!", Kimmo Mustonen concludes.
Original publication
Kimmo Mustonen, Christoph Hofer, Peter Kotrusz, Alexander Markevich, Martin Hulman, Clemens Mangler, Toma Susi, Timothy J. Pennycook, Karol Hricovini, Christine M. Richter, Jannik C. Meyer, Jani Kotakoski & Viera Skákalová; "Towards Exotic Layered Materials: 2D Cuprous Iodide"; Advanced Materials; 2021
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.





























































