"Hand in hand in hand": three catalysts solve chemical problem
Research team develops new strategy to create molecular compounds without multi-step syntheses
Advertisement
For organic synthesis, i.e. for the production of carbon-based compounds, it is important to develop synthesis processes by which the desired product can be obtained in good yield. At the same time, the processes should be sustainable: for example, they should use environmentally friendly and readily available reagents, generate little waste and consume little energy. New synthesis processes that meet these criteria can serve as a springboard for innovations - from medicinal chemistry to materials science. One example are so-called transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. In this field, a research team led by chemistry professors Frank Glorius (University of Münster) and Kendall N. Houk (University of California, Los Angeles) has now solved a problem that had been considered a challenge for years: the catalytic carbon-hydrogen (C-H) arylation of unactivated alkenes. To do so, they employed a system of three catalysts. The study was published in the inaugural issue of the newly established journal Nature Synthesis.
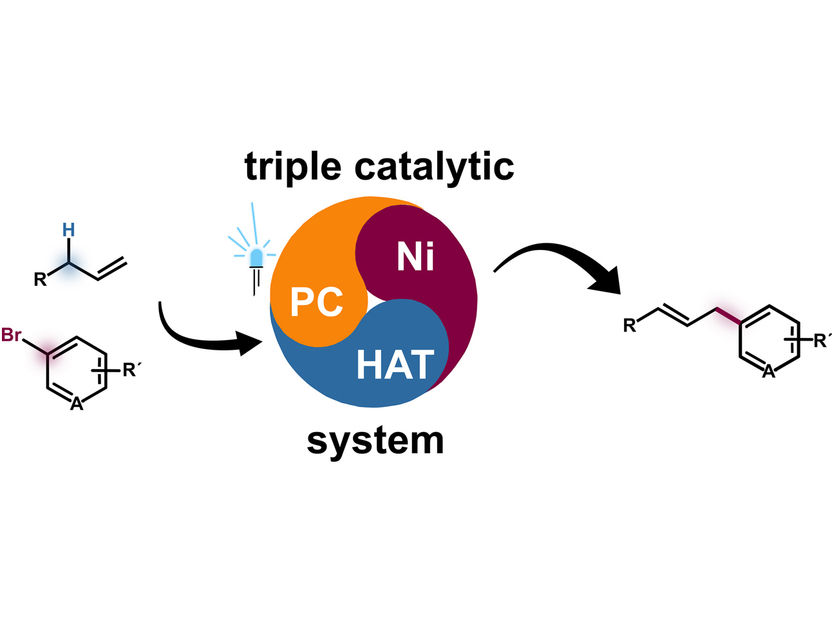
The new method for arylation of unactivated alkenes is based on a ternary nickel(Ni)-hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) photodox (PC) synergy system (schematically shown in the middle). Left side: structural formula of an aryl group (top) and an unactivated alkene, right side: arylated alkene after synthesis.
© AG Glorius – WWU Münster
Unactivated (inert) alkenes are known as starting materials for reaction processes because of their ready availability. By means of arylation, i.e. the insertion of an aryl group, the properties of the compound can be specifically modified. In the current work, the researchers have succeeded in inserting a special functional group - an aryl group - directly via catalysis, without multi-step synthesis. Chemists refer to catalysis as the acceleration and control of chemical reactions. Most catalysis reactions require only one catalyst. "In our case, however, three catalysts work together ('ternary catalysis'). This is particularly challenging, like juggling several balls," emphasizes Frank Glorius. "The three catalysts work hand in hand, so to speak." One of the catalysts is a photocatalyst that makes energy from light available for the reaction. The entire catalyst system is a so-called ternary nickel-hydrogen atom transfer photodox synergy system.
"Our redox-neutral photochemical strategy is readily applicable. We can use it to generate compounds with many different properties. Chemists talk about high functional group tolerance and breadth of application," explains Frank Glorius. "We can use it to arylate drug and natural product derivatives selectively at the allyl position. This could be used to improve efficacy or open up entirely new application possibilities."
Ken Houk adds, "In general, carbon-hydrogen bonds are inert. Using ternary catalysis allows us to selectively use a carbon-hydrogen bond for the reaction and link it to the desired partner."
In addition to the synthetic capabilities of the method, the team has been investigating the mechanistic intricacies of this ternary linkage. By combining experimental observations with density functional theory calculations, the scientists have painted a realistic picture of the elementary steps involved in the process.
By way of background, the properties of organic compounds are largely determined by so-called functional groups that sit on a framework of carbon atoms. To produce new molecules, functional groups are converted into each other. This often requires multi-step syntheses. It is more favorable to dispense with the functional group and instead produce the desired product directly from a carbon-hydrogen bond ("C-H functionalization"). However, chemists face major challenges in selecting suitable starting compounds and synthesis strategies.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.





























































