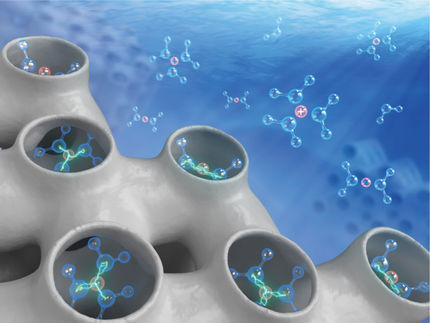
How positively and negatively charged ions behave at interfaces
When charged particles enter the boundary layer between a liquid and an electrode, they first have to strip off their water shells
How positively and negatively charged ions behave at the interface between a solid surface and an aqueous solution has been investigated by researchers from the Cluster of Excellence RESOLV at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum, its sister research network CALSOLV in Berkeley, and the University of Evry in Paris. At the SOLEIL synchrotron, they were able to use terahertz spectroscopy to observe exactly when and how the water shells around sodium and chloride ions are stripped away when voltages are applied in an electrolyte solution.

Researchers from RUB and their cooperation partners have investigated what happens at the interface between an aqueous solution and a charged surface.
© RUB, Kramer
Electrochemical double layer between electrolyte and solid interface
Electrolytes are chemical compounds in which separate ions occur. For example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) is dissolved in water, the positively charged sodium ions and the negatively charged chloride ions separate and can move freely in the solution. Due to the electrical attraction between the ions and the water molecules, a shell of water molecules forms around the individual ions – a so-called hydration shell that is stable in the solution. A layer of charge carriers forms in the immediate vicinity of the electrical boundary layer between the electrode and water. A positive and a negative charge layer are opposite each other, which is why this layer is also called an electrochemical double layer. According to chemistry textbooks, the following happens when a voltage is applied: the attraction between the electrode and the ions strips off the water shell and a charge transfer, a current, occurs.
This simple picture explains how a battery works. In the present work, the researchers from Bochum, Berkeley and Paris investigated whether it is also correct at the molecular level. They also checked whether the process is identical when negative or positive voltages are alternately applied.
Observation during the process is difficult
Observing chemical processes on a molecular level while a voltage is applied is a special experimental challenge. This is exactly what the scientists succeeded in doing in the current study with terahertz spectroscopy, which they combined with simulations. For this purpose, the researchers investigated the electrochemical double layer that forms in a NaCl solution in the immediate vicinity of a gold surface at the SOLEIL synchrotron in Paris.
Terahertz spectroscopy makes it possible to follow the stripping of the hydration shell live. The researchers also showed for the first time how the water networks on the charged gold surface change. This is essential to understand how the total energy changes in the process. “It was astonishing for us to see that the process runs differently for positive and negative charges,” sums up Professor Martina Havenith, spokesperson of RESOLV.
Asymmetric detachment of the hydration shell
The researchers found that the hydration shells of sodium and chloride ions behaved differently in the electrochemical double layer. The hydration shell of the positively charged ions was already detached at small applied voltages and the sodium ion was attracted to the electrode. For the negatively charged chloride ions, this only happened at a higher applied voltage. The team was able to attribute these differences to the behaviour of the water networks at the interface. The scientists confirmed the results with the help of complex computer simulations.
“The method and the results can now be used to investigate the crucial role of water in other interfacial processes, for example at semiconductor/electrolyte interfaces,” says Martina Havenith. The results are important for understanding and optimising electrochemical processes, for example for technological applications such as solar cell or fuel cell technologies.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.

Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.
Last viewed contents
Opium_production_in_Afghanistan

New test to better assess environmental impact of substances - Researchers developed a test that investigates whether substances can cause inheritable changes in the genome of multicellular organisms such as insects
Emerson Agrees to Purchase Virgo Valves and Controls, LTD - Strengthens Emerson Process Management’s presence in oil & gas industry
Gramicidin_S
How do you know it's perfect graphene? - The answer has been there all along
Highly sensitive quantum magnetometers on their way to industry - Quantum magnetometers for industrial use in nanoelectronics, chemical analysis and materials testing