Wet-chemical synthesis of two-dimensional metal electrocatalysts
Advertisement
With the increasingly serious global energy crisis caused by the excessive consumption of fossil fuels, developing clean, efficient, and sustainable energy conversion technologies is highly desirable. electrocatalysis is one of the most promising methods to produce clean energy. However, the wide commercial applications of electrocatalysis have been severely hindered by the sluggish kinetics in electrochemical reactions, as well as the high cost and low stability of electrocatalysts. Therefore, rational design and preparation of the highly efficient and stable electrocatalysts have become one of the most popular research directions. To date, 2D metal nanomaterials have been extensively studied in electrocatalysis due to their high surface-to-volume ratio, abundant active sites, high conductivity and superior intrinsic catalytic activities.
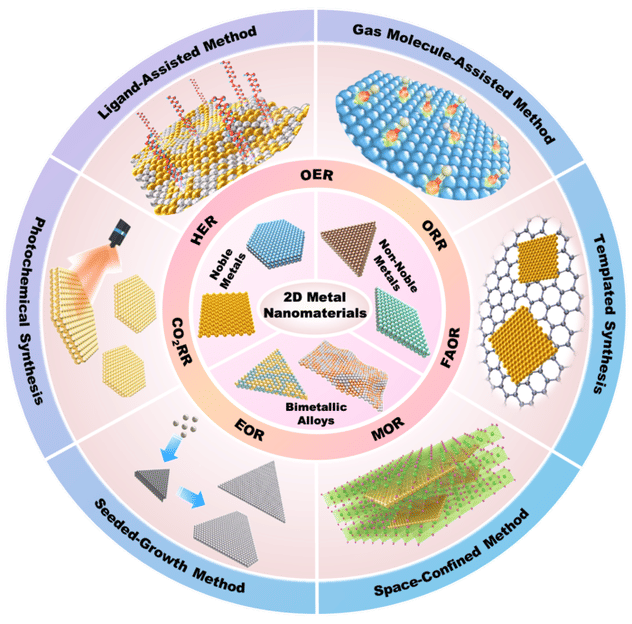
The center shows different types of 2D metal nanomaterials, including 2D noble metals, 2D non-noble metals and 2D bimetallic alloys. Arround the center, it shows seven typical electrocatalytic reactions, including HER, OER, ORR, FAOR, MOR, EOR and CO2RR. Outside, there are six typical wet-chemical synthetic methods for the preparation of 2D metal nanomaterials, such as ligand-assisted synthesis, gas molecule-assisted synthesis, templated synthesis, space-confined synthesis, seeded-growth synthesis and photochemical synthesis.
©Science China Press
As known, it is quite difficult to synthesize 2D metal nanomaterials, since 2D metallic nanostructures possess fairly large surface energy of a specific facet, which is thermodynamically unfavorable. While capping agents used in wet-chemical synthesis can greatly reduce the surface energy of nanomaterials and thus facilitate the growth along the specific crystalline orientation of metal nanocrystals. Therefore, wet-chemical synthesis using various kinds of capping agents has become the most powerful strategy to controlled synthesis of 2D metal nanomaterials with different morphology, thickness, size and crystal phase in large scale.
In a new review acticle published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at City University of Hong Kong and Nanyang Technological University gave a brief overview and personal perspectives on the recent research advances in the wet-chemical synthesis of 2D metal nanomaterials for electrocatalytic reactions.
The controlled synthesis of 2D metal nanomaterials with desired composition, size, thickness and crystal phase is essential to explore their physicochemical properties and various applications. The authors first introduced the typical wet-chemical synthetic methods for the preparation of 2D metal nanomaterials (e.g., noble metals, non-noble metals, and bimetallic alloys), such as ligand-assisted synthesis, gas molecule-assisted synthesis, templated synthesis, space-confined synthesis, seeded-growth synthesis, etc. Since 2D metal nanomaterials have aroused tremendous research interests owing to their structural merits, such as high surface-to-volume ratio, abundantly exposed surface active sites and unique electronic property, they summarized the recent progress in the usage of 2D metal nanomaterials as electrocatalysts in various electrochemical reactions, including hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR), methanol oxidation reaction (MOR), formic acid oxidation reaction (FAOR), and carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR).
Although tremendous efforts have been devoted to the preparation of 2D metal electrocatalysts, many challenges still remain. Based on the current research progress, the authors proposed some challenges and potential research directions, including 1) investigating the formation mechanisms of 2D metal nanomaterials using in situ characterizations; 2) enriching the library of 2D metal nanomaterials; 3) finely tailoring the structures of 2D metal nanomaterials.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.