Nanomaterials with laser printing
New and environmentally friendly method for synthesizing materials
In the journal Nature Communications, an interdisciplinary team from the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces presents for the first time a laser-driven technology that enables them to create nanoparticles such as copper, cobalt and nickel oxides. At the usual printing speed, photoelectrodes are produced in this way, for example, for a wide range of applications such as the generation of green hydrogen.
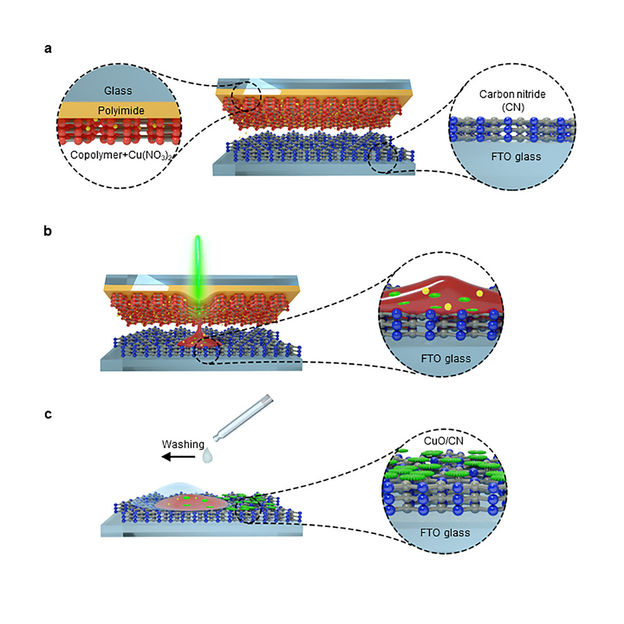
This is how the new laser-driven method works
Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung
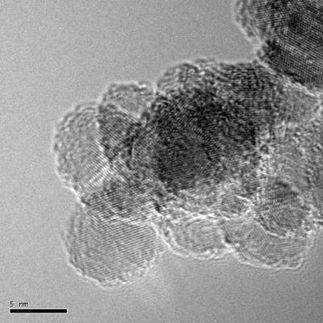
Previous methods produce such nanomaterials only with high energy input in classical reaction vessels and in many hours. With the laser-driven technology developed at the institute, the scientists can deposit small amounts of material on a surface and simultaneously perform chemical synthesis in a very short time using high temperatures from the laser. ‘When I discovered the nanocrystals under the electron microscope, I knew I was onto something big,’ says Junfang Zhang, first author of the study and doctoral researcher. The discovery turned into a new and environmentally friendly method for synthesizing materials that can, among other things, efficiently convert solar energy into electricity.
Without detours with sunlight to hydrogen: ‘Nowadays most of green hydrogen is produced from water using electricity generated by solar panels and stored in batteries. By employing photoelectrodes we can use solar light directly,’ says Dr. Aleksandr Savateev.
The newly developed principle works with so-called transition metal oxides, mainly copper, cobalt and nickel oxides, all of which are good catalysts. The special feature of these oxides is the variety of their crystal forms (nanocrystals such as nanorods or nanostars), which affect their surface energy. Each structure can have a different effect on catalytic reactions. Therefore, it is important that these nanostructures can be made targeted - or even untargeted, but repeatable. The developed technology could also be used to find quickly and efficiently new catalysts. ‘Laser dot by laser dot, we can create different catalysts side by side by simply varying the composition and conditions, and then also test them in parallel right away,’ says Dr. Felix Löffler adding, ‘But now we need to work on making the catalyst systems more persistent in all applications’.
The method
Similar to the principle of a typewriter, material is transferred from a donor to an acceptor carrier. On the former is the ‘ink’, a solid polymer, which is mixed with metal salts, the latter consists of a thin carbon nitride film on a conductive electrode. Targeted laser irradiation transfers the salts to the acceptor along with the molten polymer. The brief high temperatures cause the salts to react within milliseconds and they transform into metal oxide nanoparticles with desired morphology.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.