Mechanism Deciphered: How Organic Acids Are Formed in the Atmosphere
The acidity of the atmosphere is increasingly determined by carbon dioxide and organic acids such as formic acid. The second of these contribute to the formation of aerosol particles as a precursor of raindrops and therefore impact the growth of clouds and pH of rainwater. In previous atmospheric chemistry models of acid formation, formic acid tended to play a small role. The chemical processes behind its formation were not well understood. An international team of researchers under the aegis of Forschungszentrum Jülich has now succeeded in filling this gap and deciphering the dominant mechanism in the formation of formic acid. This makes it possible to further refine atmosphere and climate models.
Schematic of major emission sectors and primary emissions, meteorological and chemical processes, impacts to air quality and climate, and measurement and analysis tools used to analyze the effects of emissions changes.
Copyright: B. Franco et al, Ubiquitous atmospheric production of organic acids mediated by cloud droplets, Nature, May 2021, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03462-x (CC BY 4.0)
IIn Germany, we are familiar with acid rain, particularly from our experience in the 1980s. The cause of it was that nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides released into the atmosphere by human beings reacted with the water droplets in the clouds to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid. Acid rain has a pH of about 4.2–4.8, lower than that of pure rainwater (5.5–5.7), which results from the natural carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere.
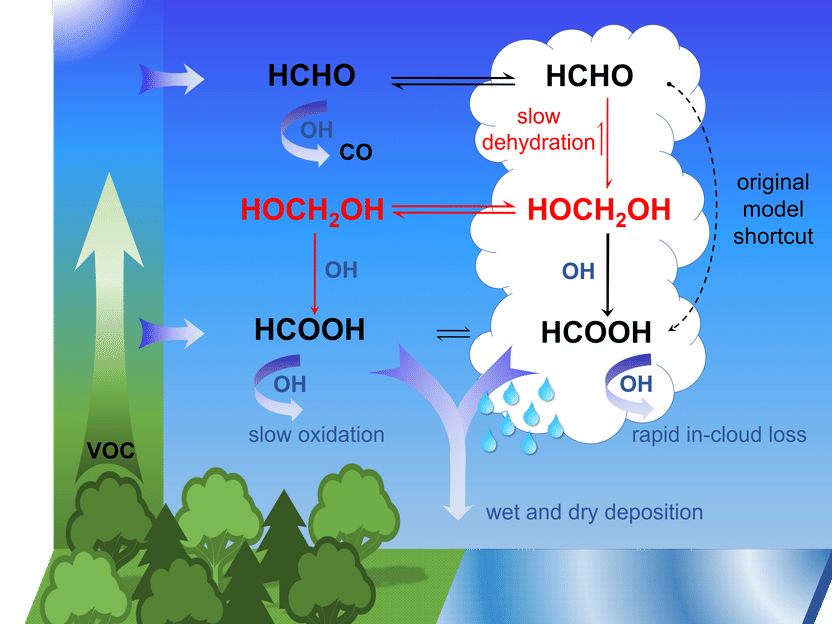
However, the chemical process that forms the bulk of the formic acid present in the atmosphere was unknown up to now. Dr. Bruno Franco and Dr. Domenico Taraborrelli from Jülich’s Institute of Energy and Climate Research – Troposphere have now deciphered it: Formaldehyde is formed naturally by photo-oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Formaldehyde reacts in cloud droplets with water molecules to form methanediol. The majority of this is outgassed and reacts with OH radicals, sometimes called the "detergent of the atmosphere", in a photochemical process to form formic acid. A smaller portion reacts with the liquid phase of the water droplets to also form formic acid that is spread by rain.
"According to our calculations, the oxidation of methanediol in the gas phase produces up to four times as much formic acid as what is produced in other known chemical processes in the atmosphere," says Domenico Taraborrelli. This amount reduces the pH of clouds and rainwater by up to 0.3, which highlights the contribution of organic carbon to the natural acidity in the atmosphere.
As a first step, the two scientists tested their theory using MESSy, a global atmospheric chemistry model, and compared the results with remote sensing data. To carry out the modelling, they used the Jülich supercomputer JURECA. Subsequent experiments in Jülich’s SAPHIR atmosphere simulation chamber confirmed the results. "We assume that the mechanism demonstrated is also active in aqueous aerosols and applies to other organic acids such as oxalic acid, which are not adequately accounted for in atmospheric chemistry models to date," says Taraborrelli. One of the effects of this could be an improved understanding of the growth of aerosol particles and the development of clouds.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




























































