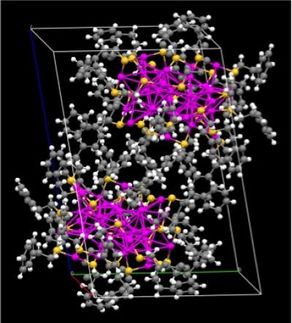
Researchers analyzed circulating currents inside gold nanoparticles
A new method facilitates accurate analysis of magnetic field effects inside complex nanostructures
Researchers in the Nanoscience Center of University of Jyvaskyla, in Finland and in the Guadalajara University in Mexico developed a method that allows for simulation and visualization of magnetic-field-induced electron currents inside gold nanoparticles. The method facilitates accurate analysis of magnetic field effects inside complex nanostructures in nuclear magnetic resonance measurements and establishes quantitative criteria for aromaticity of nanoparticles.
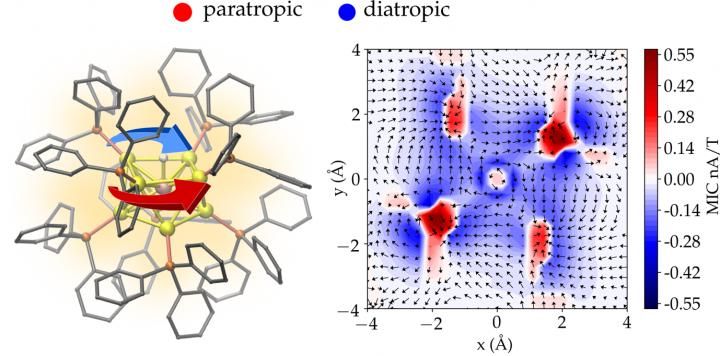
The atomic structure of a gold nanoparticle protected by phosphine molecules (left) and magnetic-field-induced electron currents in a plane intersecting the center of the particle (right). The total electron current consists of two (paratropic and diatropic) components circulating in opposite directions.
University of Jyväskylä/Omar Lopez Estrada
According to the classical electromagnetism, a charged particle moving in an external magnetic field experiences a force that makes the particle's path circular. This basic law of physics is used, e.g., in designing cyclotrons that work as particle accelerators. When nanometer-size metal particles are placed in a magnetic field, the field induces a circulating electron current inside the particle. The circulating current in turn creates an internal magnetic field that opposes the external field. This physical effect is called magnetic shielding.
The strength of the shielding can be investigated by using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The internal magnetic shielding varies strongly in an atomic length scale even inside a nanometer-size particle. Understanding these atom-scale variations is possible only by employing quantum mechanical theory of the electronic properties of each atom making the nanoparticle.
Now, the research group of Professor Hannu Häkkinen in the University of Jyväskylä, in collaboration with University of Guadalajara in Mexico, developed a method to compute, visualize, and analyze the circulating electron currents inside complex 3D nanostructures. The method was applied to gold nanoparticles with a diameter of only about one nanometer. The calculations shed light onto unexplained experimental results from previous NMR measurements in the literature regarding how magnetic shielding inside the particle changes when one gold atom is replaced by one platinum atom.
A new quantitative measure to characterize aromaticity inside metal nanoparticles was also developed based on the total integrated strength of the shielding electron current.
"Aromaticity of molecules is one of the oldest concepts in chemistry, and it has been traditionally connected to ring-like organic molecules and to their delocalized valence electron density that can develop circulating currents in an external magnetic field. However, generally accepted quantitative criteria for the degree of aromaticity have been lacking. Our method yields now a new tool to study and analyze electron currents at the resolution of one atom inside any nanostructure, in principle. The peer reviewers of our work considered this as a significant advancement in the field", says Professor Häkkinen who coordinated the research.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.