Dance of the molecules: New methods of producing tailor-made materials
Scientists observe vibrational dynamics of organic acid molecules on iron oxide surface
Advertisement
A Hamburg research team is paving the way for new methods of producing tailor-made materials: for the first time, the scientists from DESY NanoLab and the Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH) have deciphered the collective arrangement of organic acid molecules on an iron oxide surface at the atomic level. The formic acid molecules they studied perform a kind of dance in groups of three on magnetite (Fe3O4), as the team led by Andreas Stierle from DESY and Gregor Vonbun-Feldbauer from TUHH is reporting in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
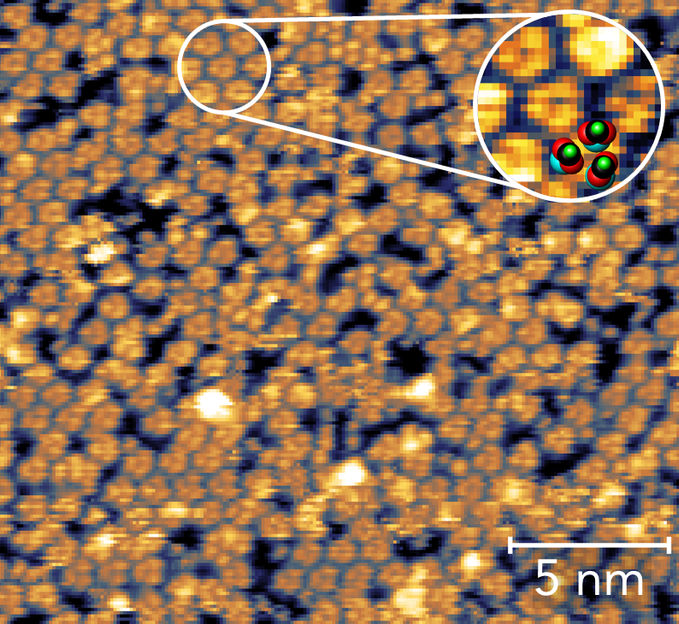
The formic acid molecules form groups of three, each about one millionth of a millimeter apart, as revealed by a scanning tunneling microscope. Zoom: Detailed image of the clusters with calculated structural model.
DESY, Marcus Creutzburg
“We are trying to understand the mechanical properties of composite materials that are inspired by nature: hard cores embedded in organic molecules,” explains Stierle, who is also a professor for nanoscience at the University of Hamburg. “If you want to tailor their mechanical properties, you need to understand what happens at the interface between these two very different classes of materials.” However, that knowledge has mostly been lacking so far.
“When oleic acid is combined with nanoparticles, the resulting materials already display many fantastic properties,” says lead author Marcus Creutzburg from DESY NanoLab. “Such composites have a particularly high strength, for example.” However, the exact details of how this comes about have not yet been determined. “We know that the acid fills the gaps between the nanoparticles, but until now we did not know what exactly happens there at the molecular level,” says Creutzburg.
The team therefore studied how formic acid behaves on a magnetite surface, as a comparatively simple model system, using a scanning tunnelling microscope, infrared spectroscopy, surface sensitive X-ray diffraction and quantum-mechanical simulations. “Formic acid is the simplest organic acid,” explains co-author Kai Sellschopp from the TUHH, who ran the computer simulations. “Oleic acid molecules are much more complex, but the end group which anchors the acid molecules to the iron oxide looks exactly like that of formic acid.”
The magnetite sample was first treated to create surface defects in the iron oxide. These make it easier for the acid molecules to attach to the surface, leading to a greater stability of the interface. The experiments and calculations show that the formic acid molecules predominantly attach themselves to the iron oxide in groups of three. Each of these groups of three are about a millionth of a millimetre (one nanometre) apart, and perform a kind of swaying dance. Because the molecules are directly coupled and thus influence each other, preferred vibrations (“eigen-modes”) of the molecules are particularly easily excited.
“This is the first example where we have been able to understand the influence of magnetite surface defects on the adsorption of an organic material at the atomic level,” says Stierle. The scientists hope to use this knowledge, together with further research, to establish a basis for systematically designing the properties of composite materials. It is also important in terms of understanding how magnetite operates as a catalyst in energy conversion processes.
Original publication
Marcus Creutzburg, Kai Sellschopp, Steffen Tober, Elin Grånäs, Vedran Vonk, Wernfried Mayr-Schmölzer, Stefan Müller, Heshmat Noei, Gregor B. Vonbun-Feldbauer, and Andreas Stierle;; "Heterogeneous Adsorption and Local Ordering of Formate on a Magnetite Surface"; The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters; 2021



























































