Tracking Topological Conditions in Graphene
How carbon-based nanostructures can get a new functionalit
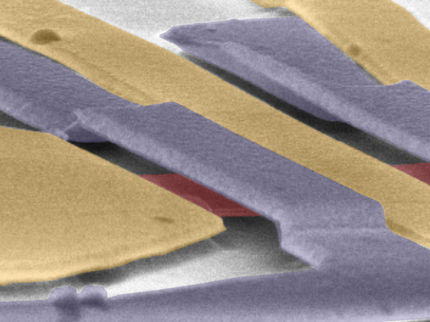
Scientists have already been able to demonstrate that graphene nanostructures can be generated by annealing of a nanostructured silicon carbide crystal for a few years. “These two-dimensional, spatially strongly restricted carbon bands exhibit a vanishingly small electrical resistance even at room temperature. They are thus ballistic,” explains Prof. Dr. Christoph Tegenkamp, Head of the Professorship of Solid Surfaces Analysis at Chemnitz University of Technology.
The scanning tunnel microscope’s measurements were made in the Solid Surfaces Analysis lab at Chemnitz University of Technology by researchers including doctoral student Thi Thuy Nhung Nguyen.
Jacob Müller, TU Chemnitz
Something similar does not happen, for example, with an expanded and perfectly two-dimensional layer of graphene. Physicists at Chemnitz University of Technology, working together with researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology (Netherlands), the Max Planck Institute in Stuttgart, and the MAX IV Laboratory in Lund (Sweden), succeeded in a better understanding of this quantum effect. “We could verify the exact structure of these so-called nanoribbons for the first time with help of an extremely high-resolution transmission electron microscope,” reports doctoral student Markus Gruschwitz from the Professorship of Solid Surfaces Analysis. Thi Thuy Nhung Nguyen, who is also completing her doctoral studies in this area, adds, “Together with measurements from the scanning tunneling microscope, the particular quantum state of this system could now be localized and spectroscopized with high resolution.”
It is important for a theoretical description of the electronic structure that the edge of the graphene nanostructure has a bond to the substrate and the bending induced by this causes a so-called strain effect. Using this model, it was also possible to explain the spin polarization of the migrating electrons. "This bending of the graphene structure has an effect similar to that otherwise found only in materials with strong spin-orbit coupling. Interestingly, graphene itself has a vanishingly small spin-orbit interaction," Tegenkamp says.
The research results were presented in the current issue of “Nano Letters”. The authors of the study are certain that the exploitation of defined curvatures will give rise to new functionalities in supposedly trivial structures and materials, and that the research field of straintronics will become further established.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.