The role of hydrophobic molecules in catalytic reactions
Optimising electrochemical processes is one of the challenges in developing technologies for renewable energies. New research findings could provide assistance here.
Advertisement
Electrochemical processes could be used to convert CO2 into useful starting materials for industry. To optimise the processes, chemists are attempting to calculate in detail the energy costs caused by the various reaction partners and steps. Researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Sorbonne Université in Paris have discovered how small hydrophobic molecules, such as CO2, contribute to the energy costs of such reactions by analysing how the molecules interact in water at the interface.
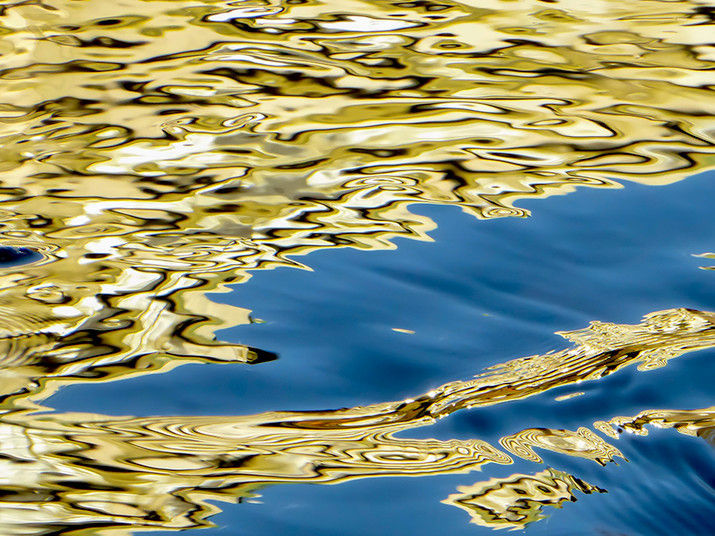

Water molecules may appear insignificant at first glance, but they have a major influence on chemical reactions. The Franco-German team is investigating what happens at the interface between water and gold.
© Elmar Weiler
To conduct the work, Dr. Alessandra Serva and Professor Mathieu Salanne from Laboratoire PHENIX at Université Sorbonne collaborated with Professor Martina Havenith and Dr. Simone Pezzotti from the Bochum Chair of Physical Chemistry II.
Crucial role for small hydrophobic molecules
In many electrochemical processes, small hydrophobic molecules react at catalyst surfaces that often consist of precious metals. Such reactions often take place in an aqueous solution, whereby the water molecules form what are known as hydration shells around the other molecules: they accumulate around the other molecules. The water surrounding polar, i.e. hygroscopic molecules behaves differently compared to the water surrounding non-polar molecules, which are also referred to as hydrophobic. The Franco-German research team was interested in this hydrophobic hydration.
Using molecular dynamic simulations, the researchers analysed the hydrophobic hydration of small molecules such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or nitrogen (N2) at the interface between the gold and water. They showed that the interaction of water molecules in the vicinity of small hydrophobic molecules makes a crucial contribution to the energy costs of electrochemical reactions.
Model for calculating energy costs expanded
The researchers implemented these findings in the Lum-Chandler-Weeks theory. This allows the energy required to form water networks to be calculated. “The energy costs for hydrophobic hydration were calculated for the bulk in the previous model. This model has now been expanded here to hydrophobic molecules near interfaces. This case was not included before,” explains Martina Havenith, the Speaker of the Ruhr Explores Solvation Cluster of Excellence, RESOLV for short, at RUB. The adapted model allows the energy costs for hydrophobic hydration to now be calculated at the interface between gold and water based on the size of the hydrophobic molecules. “Due to the water contribution, the size of the molecules plays an important role in the chemical reactions at these interfaces,” says Dr. Simone Pezzotti from the Bochum Chair of Physical Chemistry II.
For instance, the model predicts that small hydrophobic molecules would tend to accumulate at the interface based on the interactions with the water, while larger molecules would remain further away in the solution.