Compression or strain – the material expands always the same
Regardless if strained or compressed, the new material always expands
An international research team led by chemist Prof. Thomas Heine of TU Dresden has discovered a new two-dimensional material with unprecedented properties: regardless if it is strained or compressed, it always expands. This so-called half-auxetic behavior has not been observed before and is therefore very promising for the design of new applications, especially in nano-sensorics.
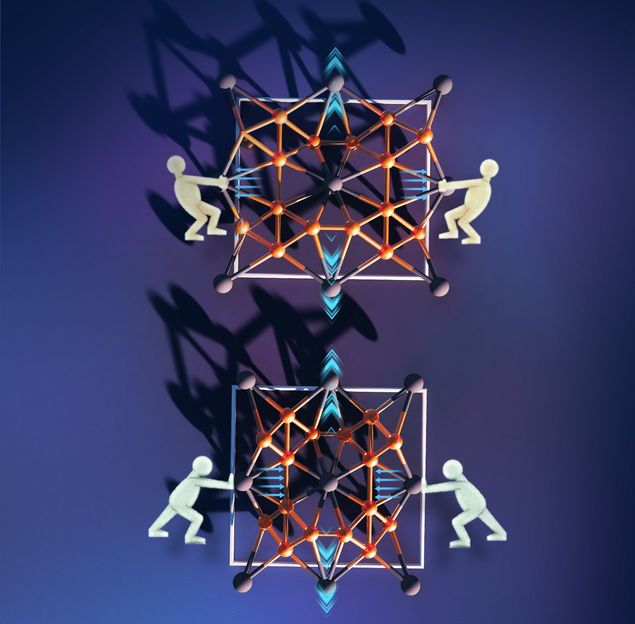
Regardless if strained or compressed, the new material always expands.
© Thomas Heine et al.
If you stretch an elastic band, it becomes thinner - a physical behavior that applies to most "common" materials. Since the 20th century, an opposite behavior has been known in materials research: The so-called auxetic (from ancient Greek auxetos, meaning 'stretchable') materials expand in the direction orthogonal to the strain. Likewise, they shrink when they are compressed. Scientifically, they are characterized by a negative Poisson's ratio. Probably the best known and oldest application of unusual Poisson's ratios is the bottle cork, which has a Poisson's ratio of zero. This has the effect that the cork can be put into the thinner neck of the bottle.
Due to their special properties, auxetic materials allow for completely new functionalities and design solutions for a variety of innovative products with adjustable functional properties, including applications in medical technology or in the development of protective equipment such as bicycle helmets or safety jackets.
Thomas Heine, Professor of Theoretical Chemistry at TU Dresden, and his team have now discovered a previously unknown phenomenon. Based on borophene, an atomically thin configuration of the element boron, a stable form was found by adding palladium, yielding the chemical composition PdB4. The computational modelling shows that this material behaves like an auxetic material under strain, but expands like an ordinary material under compression. In other words, regardless if it is strained or compressed, the material always expands.
"In addition to thorough characterization in terms of stability, mechanical and electronic properties of the material, we have identified the origin of this half-auxetic character and believe that this mechanism can be used as a design concept for new half-auxetic materials," explains Prof. Heine, "These novel materials could lead to innovative applications in nanotechnology, for example in sensing or magneto-optics. A transfer to macroscopic materials is equally conceivable."
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.