Vibrating 2D Materials
An international research team now has determined for the first time how strongly 2D materials vibrate when electronically excited with light
Current electronic components in computers, mobile phones and many other devices are based on microstructured silicon carriers. However, this technology has almost reached its physical limits and the smallest possible structure sizes.
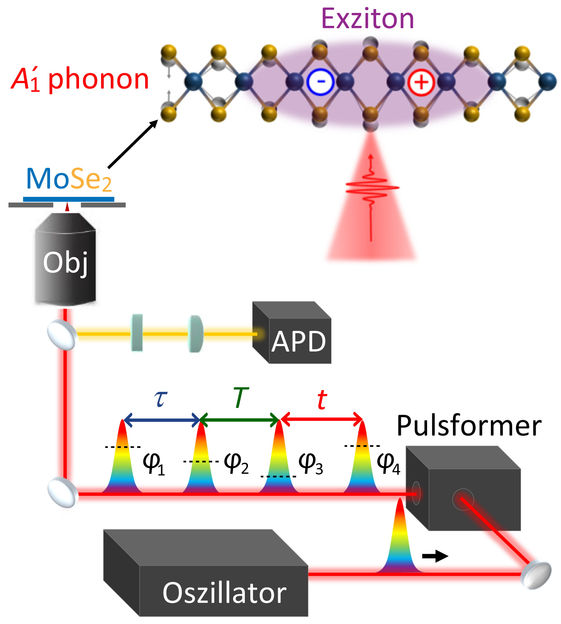
Scheme of the experiment.
Donghai Li, University of Würzburg
Two-dimensional (2D) materials are therefore being intensively researched. One can imagine these materials as extremely thin films consisting of only one layer of atoms. The best known is graphene, an atomically thin layer of graphite. For its discovery, Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010.
While graphene consists purely of carbon, there are numerous other 2D compounds that are characterised by special optical and electronic properties. Countless potential applications of these compounds are currently being researched, for example for use in solar cells, in micro- and optoelectronics, in composite materials, catalysis, in various types of sensors and light detectors, in biomedical imaging or in the transport of drugs in the organism.
Light energy can make 2D materials vibrate
For the function of these 2D compounds, one exploits their special properties. "It is important to know how they react to excitation with light," says Professor Tobias Brixner, head of the Chair of Physical Chemistry I at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany.
In principle, 2D materials are electronically excited just like ordinary silicon solar cells when sufficient light energy hits them. However, the energy can cause the atomically thin layer to vibrate at the same time. This in turn influences the optoelectronic properties.
Strength of exciton-phonon coupling is difficult to determine
Until now, it was unknown how strongly light excites such oscillations in a 2D material at room temperature. Now, in an international collaboration, a team led by Tobias Brixner has succeeded for the first time in determining the strength of the oscillation excitation upon light absorption in a 2D material – namely in a "transition metal dichalcogenide" – at room temperature.
"This quantity, known in technical jargon as exciton-phonon coupling strength, is difficult to determine because at room temperature the absorption spectrum is very much 'smeared out' and no individual spectral lines can be separated," says the JMU physicist and physical chemist.
Postdoc developed coherent 2D microscopy
Now, however, postdoctoral researcher Dr Donghai Li in Würzburg has developed the method of "coherent 2D microscopy". It combines the spatial resolution of a microscope with the femtosecond time resolution of ultra-short laser pulses and with the multi-dimensional frequency resolution. This allowed Li to quantify the influence of the oscillations.
Brixner explains: "Surprisingly, it turned out that the exciton-phonon coupling strength in the investigated material is much greater than in conventional semiconductors. This finding is helpful in the further development of 2D materials for specific applications."
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.