'Swiss Army knife' catalyst can make natural gas burn cleaner
Lowering the combustion temperature for methane
Advertisement
Reza Shahbazian-Yassar, professor of mechanical and industrial engineering at the University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues facilitated the development of a cutting edge "Swiss Army knife" catalyst made up of 10 different elements - each of which on its own has the ability to reduce the combustion temperature of methane - plus oxygen. This unique catalyst can bring the combustion temperature of methane down by about half - from above 1400 degrees Kelvin down to 600 to 700 degrees Kelvin.
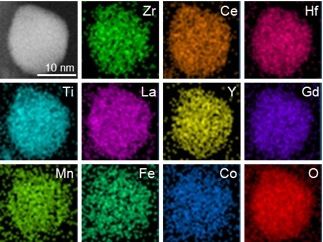
The elements that make up the metal oxide nanoparticle catalyst
Zhennan Huang
In previously-published research, Shahbazian-Yassar and colleagues demonstrated the ability to create multi-element nanoparticle catalysts, known as high entropy alloys using a unique shock-wave technique. Before this, materials scientists didn't make serious attempts to create nanoparticles out of more than three elements because of the tendency of each elements' atoms to separate from each other and become useless.
Taking advantage of the unique real-time, high-temperature electron microscopy system at UIC, Shahbazian-Yassar's team showed that high entropy nanoparticles made up of 10 metal oxides were highly stable at temperatures up to 1,073 degrees Kelvin and the individual elements were distributed evenly throughout each nanoparticle forming a single, solid-state stable crystalline structure.
Their metal oxide alloy contained various mixtures of transition metals, which are rare-earth elements, and noble metals plus oxygen.
"It is almost impossible to maintain a perfect mix of these elements in a solid phase due to the differences in atomic radius, crystal structure, oxidation potential, and electronic properties of the elements," said Zhennan Huang, a Ph.D. student in Shahbazian-Yassar's lab and co-first author in the paper. "But we were able to show that this is possible."
"Among multiple alloys with multiple elements that we created, the particles made of 10 elements not only were most effective in reducing the combustion point of methane gas but also the most stable at those temperatures," said Shahbazian-Yassar, who is a corresponding author on the paper.
The researchers believe the catalyst could be used to reduce the output of harmful greenhouse gases produced by burning natural gas in individual households, to power turbines and even in cars that run on compressed natural gas.




























































