Nano-infused filters prove effective
Rice scientists build better catalyst with nanotube membranes
Advertisement
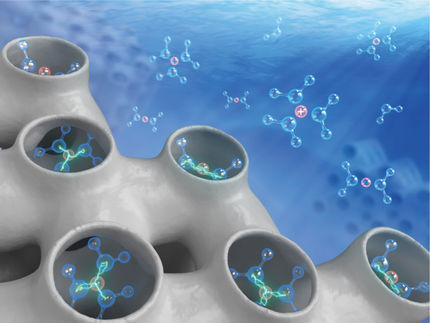
rice University researchers and their colleagues in Finland and Hungary have found a way to make carbon nanotube membranes that could find wide application as extra-fine air filters and as scaffolds for catalysts that speed chemical reactions.
The results reported in the journal ACS Nano show how such filters can remove up to 99 percent of particulates with diameters of less than a micrometer – or a millionth of a meter. (A human hair is about 100 micrometers wide.)
Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), a team led by Rice's Robert Vajtai, a faculty fellow in mechanical engineering and materials science, created devices that, at the start of the process, look like tiny showerheads. After 30 minutes in the CVD furnace, the laser-created holes in these silicon dioxide templates fill up with a forest of carbon nanotubes through which only particles on the nanometer scale can pass.
When the tubes are functionalized with catalytic chemicals, particles enter one side of the filter in one form and come out as another. The process is similar to that used by catalytic converters in cars, which convert carbon monoxide into a less-toxic mix of carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water.
"Even when the holes are larger than the particle itself, it can be a very effective filter," Vajtai said. "The basic idea is you have this carbon nanotube forest. The gas flows through, and because of the very small distance between the tubes, gas atoms have to hit many of them before they get out the other side.
"This very strong interaction, compared to macroscopic materials and even some microscopic materials, provides a very good way to make a catalyst template or a filter that is much more effective than a HEPA (high-efficiency particulate-absorbing) filter you can buy at the store," he said.
The filters' permeability depends strongly on how long the nanotubes are allowed to grow, which determines their length and density. The team tested the filters' ability to act as catalysts by depositing palladium onto the nanotubes and using them to turn propene into propane, a benchmark test for catalysis. They found the activated membranes "showed excellent and durable activity," according to the paper.
Most read news
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.