Animal-free method predicts nanoparticle toxicity for safer industrial materials
A step closer to safe-by-design material development
Researchers at Helmholtz Zentrum München together with scientists across Europe developed a novel animal-free method to predict the toxic effect of nanoparticles to the human lung. The method aims to enable the safety-by-design development of safer industrial materials.
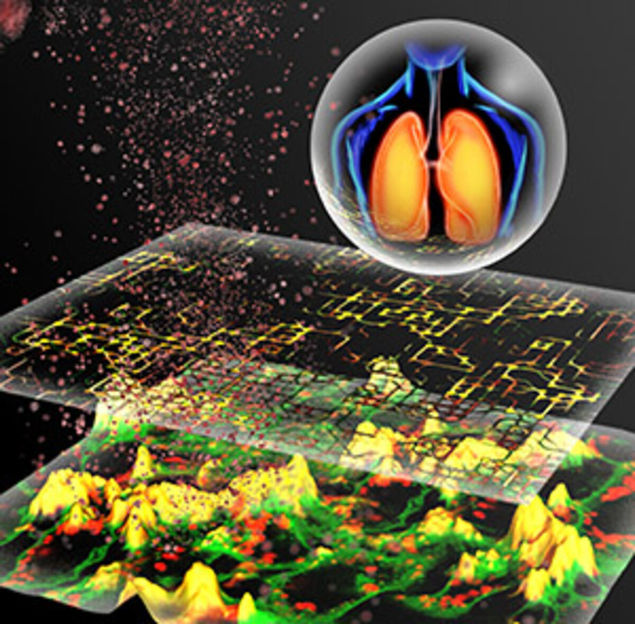
In silico modeling of particle-cell interactions for the prediction of respiratory nanoparticle toxicity (graphical display).
© Helmholtz Zentrum München
Our lungs are exposed to a multitude of hazardous airborne particles on a daily basis. Nanoparticles, due to their small size, may reach the sensitive alveolar region of the human lung and trigger inflammation even after a single inhalation leading to severe diseases such as heart disease, brain damage and lung cancer for prolonged exposure. In manufacturing, toxic nanoparticles may be released into the environment during the production, processing, degradation or combustion of materials. Despite advances in models for nanotoxicology, currently neither in vitro nor in silico testing tools can reliably predict adverse outcomes or replace in vivo testing. In order to facilitate the introduction of safer materials into our lives, novel testing strategies are needed to predict the potential toxicity of industrial nanoparticles before and during the manufacturing process.
Unlocking the cellular mechanisms
At Helmholtz Zentrum München, the research group of Dr. Tobias Stöger is focusing on an improved mechanistic understanding of the interactions between nanoparticles and lung cells, especially in view of the resulting inflammation. In cooperation with partners from the SmartNanoTox EU project, the research group discovered that for certain materials the long-lasting inflammatory response to a single exposure to a nanoparticle can originate from two cellular key events which were so far unknown: First, the quarantining process which is the deposition of excreted immobile composites of the nanoparticles wrapped with biological molecules on the cell surface. Second, the so-called nanomaterial cycling which entails the movement of the nanoparticles between different alveolar lung cell types.
“With these new insights, we developed a deeper comprehensive approach on how an inflammatory response in the lung originates from particle-cell interactions. Being able to pinpoint the origin to these two key events and quantitatively describe them was a breakthrough as it helped us built our prediction method”, says Stöger.
A step closer to safe-by-design material development
Using only a small set of data from in vitro measurements and by combining it with in silico modeling, the researchers gathered insights on the toxicity of nanoparticles and managed to predict the spectrum of lung inflammation (from acute to chronic) associated with a range of 15 selected materials. Stöger adds: “Being able to make such a prediction means that we can move a step closer to a safe-by-design material development. This will have profound implications on the safety, speed and cost-effectiveness of new materials.”
Additional benefit: Animal-free testing
Currently, safety testing relies heavily on animal studies. While animal experimentation is still indispensable for mechanistic and chronic toxicological studies, they are less suited for predictive tests within a safe-by-design production of new materials. This study introduces an alternative animal-free testing strategy, capable for high-throughput testing and connectable with in silico modelling.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.