How charges move in solar cells
An understanding of microscopic processes in perovskite solar cells can lead to increased efficiency
Advertisement
When the sun rises, a complex dance begins in perovskite solar cells - a type of solar cell that can supplement or replace existing silicon solar cells in the future: Electrons are supplied with energy by light and move. Where electrons move, they leave holes. At the same time, ions move around in the perovskite material. An understanding of this complex dance - i.e. how exactly these particles move - can help to increase the efficiency of solar cells. Gert-Jan Wetzelaer, group leader at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) in Mainz, and his team have used a combination of experiments and computer simulations to get closer to the microscopic processes.
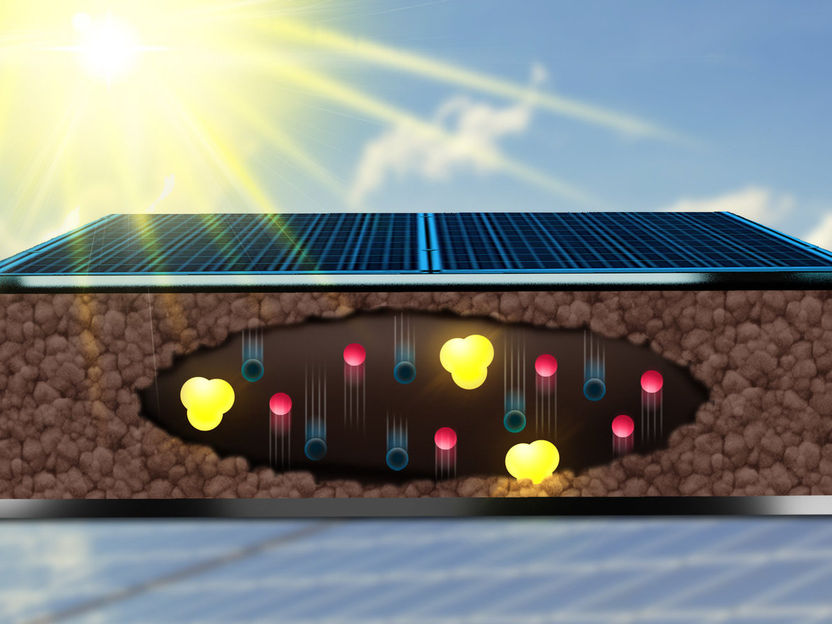
A complex dance: In a perovskite solar cell, electrons, holes and ions move and influence each other.
© MPI-P
When light falls on a solar cell, its energy is transferred to electrons, which in turn can supply a device with electricity - this is the simple explanation of solar cells. But microscopically speaking, many different processes take place: When the electron is moved, it leaves a hole - which acts like a positive charge and moves in the opposite direction through the solar cell material – a semiconductor. At the same time, novel solar cells based on new perovskite materials additionally contain charged atoms, so-called ions, which also move around in the solar cell and interact with electrons and holes.
In this complex interplay, it is desirable to transport electrons or holes to the contacts of the solar cell as quickly as possible - because the longer they remain in the material, the greater the probability that they will lose their energy by other means and return it to the material. To optimize this time, it is important to have precise knowledge of the so-called "mobility" - i.e. the speed - of electrons and holes. However, this was difficult to access in a working solar cell because of this complex interplay between electrons, holes and slow-moving ions.
Gert-Jan Wetzelaer and his research colleagues have first measured the speed and the amount of the additional ions present in the perovskite material. With this information they were able to perform computer simulations, which could be used to obtain the electron and hole mobility from electrical current measurements. They have thus discovered that the holes in particular move more slowly than originally thought.
"These results are very important in order to be able to optimize the efficiency of solar cells in the future," says Wetzelaer. "After all, if we understand more precisely the exact processes that limit the mobility of electrons and holes, we can look for ways to circumvent them".