Green Chemistry: Sustainable p-xylene production
Green, sustainable and biodegradable polymers
Lemonade, juice and mineral water often come in PET bottles. While these are practical and functional, their production is complex and not necessarily sustainable. The starting material for terephthalic acid, which is used to produce saturated polyesters such as PET (Polyethylene terephthalate), is p-xylene pXL. To this day, the production of pXL is still based on fossil raw materials. pXL is considered one of the most important building blocks in the polymer industry. In 2015, around 37 million tons of pXL were used, mainly for the production of PET and other polyester fibers. These figures show very clearly that there is a great need for the selective synthesis of pXL from renewable raw materials.
Synthesis of p-xylene from waste biomass and its further conversion into biopolymers.
Green Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1039/D0GC01517B Published by The Royal Society of Chemistry
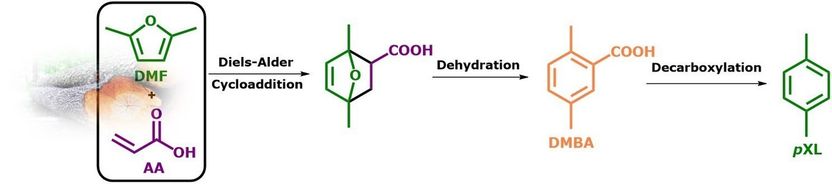
Representation of “Three-in-one” reaction in continuous flow for the synthesis of pXL from waste biomass derivable DMF and AA. J. A. M. Mesa, F. Brandi, I. Shekova, M. Antonietti and M. Al-Naji, “p-Xylene from 2,5-dimethylfuran and acrylic acid using zeolite in continuous flow system”
Green Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1039/D0GC01517B Published by The Royal Society of Chemistry
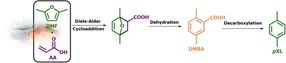
Three-in-one heterogeneously-catalyzed reaction
The "Biorefinery and Sustainable Chemistry" team at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam has now developed a green and sustainable approach to selective pXL synthesis. This approach involves a heterogeneously catalyzed three-in-one reaction: Diels-Alder cycloaddition of biologically derived 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF) to acrylic acid (AA), dehydration to form the phenyl ring and final decarboxylation to pXL in a continuous flow system.
Green, sustainable and biodegradable polymers
The result of this process is a very valuable product mixture. This consists of 83% pXL and 17% 2,5-dimethylbenzoic acid (DMBA), which can be easily separated due to its boiling points. This new approach will enable the synthesis of green, sustainable and biodegradable polymers in the future, for example the replacement of packaging materials for plastic bottles, films and textile fibers derived from fossil raw materials.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.