A new synthesis method for three-dimensional nanocarbons
Connecting carbon by catalysis to create octagonal structures
A team of scientists led by Kenichiro Itami, Professor and Director of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM), has developed a new method for the synthesis of three-dimensional nanocarbons with the potential to advance materials science.
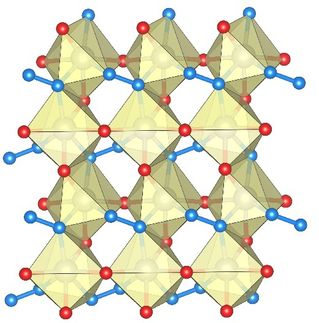
Three-dimensional nanocarbons, next-generation materials with superior physical characteristics which are expected to find uses in fuel cells and organic electronics, have thus far been extremely challenging to synthesize in a precise and practical fashion. This new method uses a palladium catalyst to connect polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to form an octagonal structure, enabling successful three-dimensional nanocarbon molecule synthesis.
Nanocarbons, such as the fullerene (a sphere, recipient of the 1996 Nobel Prize), the carbon nanotube (a cylinder, discovered in 1991) and graphene (a sheet, recipient of the 2010 Nobel Prize) have attracted a great deal of attention as functional molecules with a variety of different properties. Since Mackay et al. put forward their theory in 1991, a variety of periodic three-dimensional nanocarbons have been proposed. However, these have been extraordinarily difficult to synthesize. A particular challenge is the eight-membered ring structure, which appears periodically, necessitating an efficient method for its synthesis. To do so, Dr Itami's research team developed a new method for connecting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using a palladium catalyst to produce eight-membered rings via cross-coupling, the first reaction of its type in the world.
The success of this research represents a revolutionary achievement in three-dimensional nanocarbon molecule synthesis. It is expected to lead to the discovery and elucidation of further novel properties and the development of next-generation functional materials.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.
Last viewed contents
ABB wins $27 million solar orders in Italy

Fighting global warming with tamarind polymers - Start-up wins ISC3 Innovation Award 2023

New ways to fine tune electrochemistry - Scientists have found new paths to steer and optimize electrochemical processes
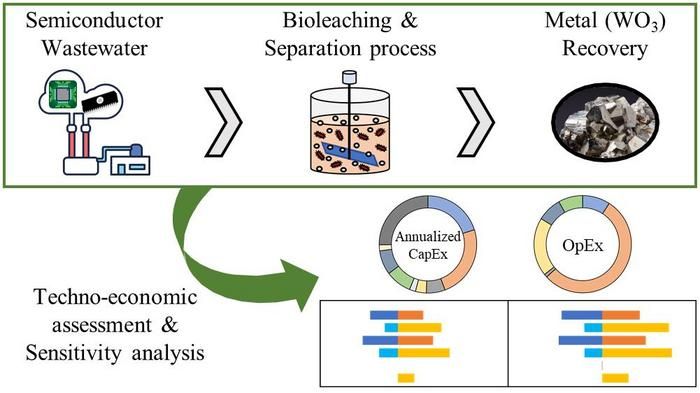
Finding pearls in the mud: eco-friendly tungsten recovery from semiconductor waste

“Dictionaries” make fluorescence-based data for integrative structure models and their dynamics accessible - 3D structures of biomolecules
Making high-temperature superconductivity disappear to understand its origin - Scientists have collected evidence suggesting that a purely electronic mechanism causes copper-oxygen compounds to conduct electricity without resistance at temperatures well above absolute zero