Superconduction: Cuprate-like behavior in a nickel-oxide film
Two-dimensional electron gas discovered
Advertisement
superconductors transmit electric current without loss at any distance and play an important role in quantum computers and medical imaging. But the stars among the electrical conductors work exclusively at extremely low temperatures. Since the discovery of high-temperature superconducting cuprates in 1986, scientists have been searching for similar behavior in other materials. It was not until 2019 that superconductivity was reported in a nickel oxide, but the underlying mechanism is still unclear. Theoretical physicists from the Center for Nanointegration (CENIDE) at the University of Duisburg-Essen (UDE) have studied the electronic properties and found a possible explanation.
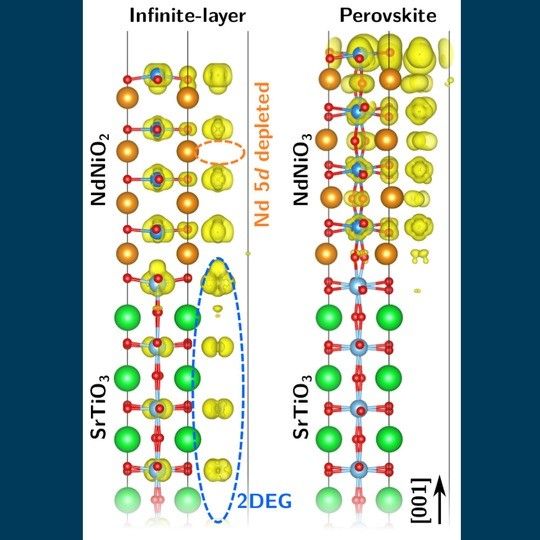
Side view of the infinite layer (left) and perovskite structure (right) on SrTiO3. Only the infinite layer film produces a two-dimensional electron gas at the interface (outlined in blue).
(c) CENIDE, Pentcheva/Geisler
Since bulk neodymium nickel oxide (NdNiO2), which exhibits an analogous crystal structure and valence electron number as the cuprates, does not show superconductivity, Prof. Rossitza Pentcheva and Dr. Benjamin Geisler focused on the role of the film geometry. They simulated a 1.5 nanometer thin layer of this so-called infinite-layer nickelate on a strontium titanate substrate (SrTiO3) in comparison to a perovskite (NdNiO3) film based on quantum-mechanical simulations at the supercomputer MagnitUDE.
Two-dimensional electron gas discovered
Despite the fact that both systems have a charge mismatch at the interface, a major difference appears in accommodating it: Only in the infinite-layer case does the charge mismatch lead to the formation of a two-dimensional electron gas at the interface. "It is known from other materials combinations that such a two-dimensional electron gas can be superconducting" explains Pentcheva. Moreover, in contrast to the bulk, the infinite-layer film shows a cuprate-like electronic behavior, indicating that the film geometry may play a significant role in the emergence of superconductivity.
The more that is known about the origin of superconductivity, the better the chances are that the sought-after property can be specifically induced in tailor-made material systems, even at room temperature.