General descriptor sparks advancements in dye chemistry
Move away from inefficient trial-and-error developments to quantitatively design luminescent materials
Advertisement
There is an ongoing demand in biological research to accelerate the development of fluorescent probes based on the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) mechanism. By modulating PET formations, these probes significantly change fluorescence intensities, allowing a convenient route to monitor analytes or environmental changes with high sensitivity, vivid visibility and excellent spatiotemporal resolution.
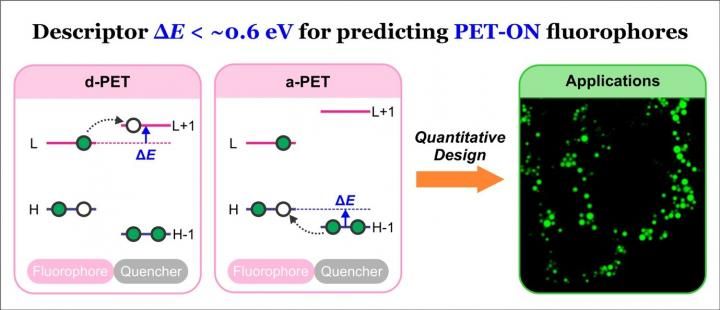
Researchers from SUTD, DICP, and POSTECH developed a theoretical descriptor ΔE for predicting PET-based fluorescence probes; utilizing this descriptor, they quantitatively designed fluorescent stains of lipid droplets and mitochondria for live-cell bioimaging.
SUTD
However, the quantitative design of fluorescence probes based on the PET mechanism continues to be a challenging task as dye chemistry is still largely based on trial-and-error.
To address this challenge, an international team of researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics in China (DICP), and Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) in South Korea have developed a theoretical descriptor, ΔE, to quantitatively design PET fluorescence probes.
The team established the ΔE descriptor by performing quantum chemical calculations on around 140 existing PET probes and analysing the correlations between their electronic structures and their quantum yields, or otherwise known as the efficiency of generating fluorescence.
The researchers also demonstrated that the descriptor was applicable to several families of fluorophores such as BODIPY, fluorescein, and rhodamine derivatives. Based on the descriptor, they accurately predicted and successfully developed wash-free fluorescent stains of lipid droplets and mitochondria for live cell bioimaging.
They were also able to quantitatively design fluorophores with the aggregation induced emission properties. The establishment of this theoretical descriptor enables chemists and biologists to quantitatively search and design new PET-based fluorescence probes.
"Our research goal is to transform the dye chemistry from trial-and-error to molecular engineering, with the state-of-art research tools such as chemical big data and quantum chemical calculations. As we continue to closely work with dye chemists to achieve this goal, we will also be developing high-performance fluorescent materials along the way," said Assistant Professor Liu Xiaogang from SUTD.