A chemical embrace from the perfect host
An industrial process that currently consumes vast amounts of energy in petrochemical plants around the globe could be replaced by an alternative process so efficient that it requires no heating or elevated pressure.
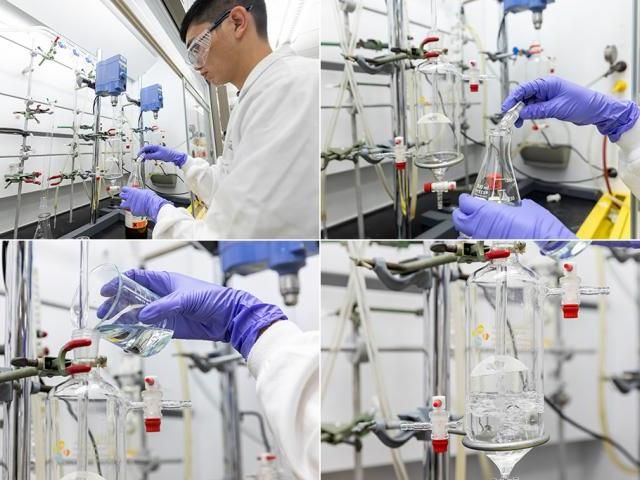

Gengwu Zhang performs the separation experiment using two extraction towers.
© 2020 KAUST
Niveen Khashab from KAUST's Advanced Membranes and Porous Materials Center and her colleagues have developed a new way to separate derivates of benzene called xylenes.
"Discussions with industry to implement the technology are already underway," Khashab says.
Xylenes come in three different forms, known as isomers, which differ from each other only in the location of a single carbon atom. Xylenes are used in many large-scale applications, including in polymers, plastics and fibers, and as fuel additives, but many uses rely on just one of the three isomers. Because the isomers are so similar, their physical properties, such as boiling point, are very close, which makes separating them energetically expensive.
"Every year, the global energy costs of separating these isomers using distillation is about 50 gigawatts, enough to power roughly 40 million homes," says Gengwu Zhang, a postdoc in Khashab's team and first author of the study. "We wanted to develop a method with high efficiency and low energy consumption to separate and purify these isomers for the petrochemical industry."
To draw apart the xylene isomers, Khashab and her team used doughnut-shaped molecules called cucurbiturils. The hole in the middle of these molecules can host smaller molecules inside it. The hole in the middle of cucurbit[7]uril is the ideal size for hosting the ortho-isomer of xylene, the team showed. Using a process called liquid-liquid extraction, the team used cucurbit[7]uril to separate ortho-xylene from the other isomers. "We could separate ortho-xylene with more than 92 percent specificity after one extraction cycle," Zhang says. "Unlike previous methods, our method is performed under ambient temperature and pressure, which means very low energy consumption and easy operation," he adds.
The whole process was designed to be readily adopted in the existing plants of petrochemical companies, Khashab explains. "Liquid-liquid extraction towers are already used in industry and so it is relatively easy to incorporate our material in this setup," she says. In addition, cucurbit[7]uril is inexpensive, commercially available or easily made, and highly stable compared to most porous materials.
"We have already shown that we can separate xylene from commercial oil samples at scales of up to 0.5 liters," Khashab adds. "We are in touch with Saudi Aramco to take this process to industrial implementation."
The team is also examining other applications for this separation process, Zhang says.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Extraction
Extraction is a fundamental process in the chemical laboratory that enables specific components to be isolated and concentrated from a mixture. Whether it's extracting active ingredients from natural products, removing impurities from synthesis products, or preparing analytical samples, extraction is a key step in achieving precise and efficient results in chemical research and analysis.

Topic world Extraction
Extraction is a fundamental process in the chemical laboratory that enables specific components to be isolated and concentrated from a mixture. Whether it's extracting active ingredients from natural products, removing impurities from synthesis products, or preparing analytical samples, extraction is a key step in achieving precise and efficient results in chemical research and analysis.