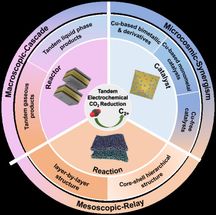
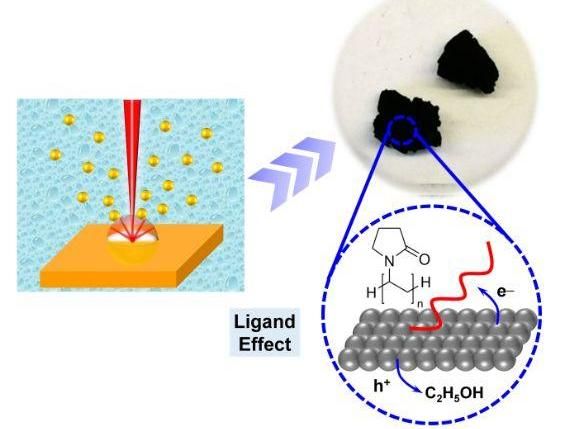
Manipulating ligands
A new dimension for promoting electrocatalysis performance by noble metal aerogels
Noble metal aerogels (NMAs) are an emerging class of porous materials embracing nano-sized highly-active noble metals and porous structures, displaying unprecedented performance in diverse electrocatalytic processes. However, various impurities, particularly organic ligands, are often involved in the synthesis and remain in the corresponding products, hindering the investigation of the intrinsic electrocatalytic properties of NMAs. On the other hand, the presence of organic ligands is generally regarded detrimental to the catalytic process because they can block the active sites. However, the authenticity of this fact has not yet been verified in NMA systems because of the lack of way to impart ligands in clean NMAs via a controlled manner.
In light of cleanliness of laser-produced metal nanoparticle precursors, surface-clean noble metal aerogels are created. The intrinsic electrocatalytic properties of NMAs are elucidated, and ligand-modulated electrocatalytic properties are disclosed for electro-oxidation of ethanol. Therefore, the work offers a new dimension for devising high-performance electrocatalysts for NMAs and other material systems.
(c) Ran Du
Ran Du from China is a Alexander von Humboldt research fellow working as postdoc in the physical chemistry group of Professor Alexander Eychmüller at TU Dresden since 2017. In collaboration with Prof. Stephan Barcikowski from the University of Duisburg-Essen, they recently created surface-clean noble metal aerogels by using laser-produced nanoparticles and thus, revealing a new dimension for enhancing electrocatalysis performance for electro-oxidation of ethanol (the anode reaction for direct ethanol fuel cells) by modulating ligand chemistry.
Ran Du and his team prepared various inorganic-salt-stabilized metal nanoparticles by laser ablation, which serve as organic-ligand-free precursors. In this way, they fabricated various impurity-free NMAs (gold (Au), palladium (Pd), and gold-palladium (Au-Pd) aerogels. In this light, the intrinsic electrocatalytic properties of NMAs were unveiled. In addition, these clean gels were used as a platform to deliberately graft specific ligands, by which the ligand-directed modulation of electrocatalytic properties was unambiguously demonstrated. The underlying mechanisms were found to be attributed to electron density modulations posed by different ligands, where the electrocatalytic activity of ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR) has been positively correlated with the oxidation state of the metals. In this regard, the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)-modified Au-Pd bimetallic aerogel delivered a prominent current density of 5.3 times higher than commercial Pd/C (palladium/carbon) and 1.7 times higher than Au-Pd pristine aerogels.
"With this work, we not only provide a strategy to fabricate impurity-free NMAs for probing their intrinsic properties, but also offer a new dimension for devising high-performance electrocatalysts by revisiting the effects of the ligands", assumes Ran Du.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
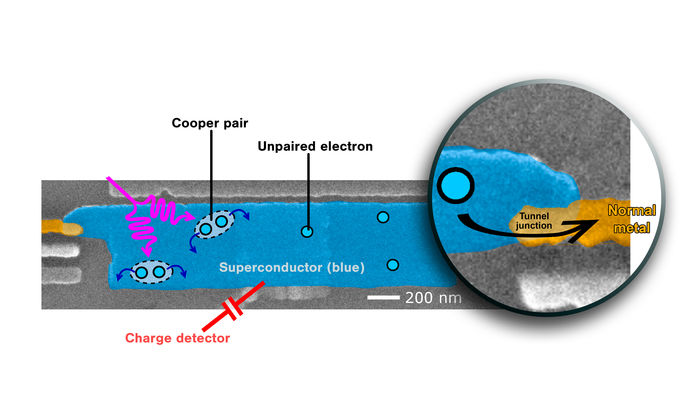
Moments of silence point the way towards better superconductors - Temporal patterns could show us how to reduce noise in superconductor devices
Pharmaceutical_company
3D imaging study reveals how atoms are packed in amorphous materials - UCLA-led research could revise a 70-year-old model of how the fundamental building blocks of substances are assembled
Air Liquide: start-up of a new unit in Tatarstan
BASF to increase prices for polyalcohols in Europe
Priscilla_White_(physician)
Attwater's_Prairie_Chicken